Lock, Key, and Command: The Magic of Secure Shell
Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol used for secure data communication, remote shell services, and command execution. It's an indispensable tool for system administrators, developers, and anyone who needs secure remote access to servers and other networked devices. With SSH, you can manage your servers from anywhere in the world, transfer files securely, and even tunnel traffic through encrypted channels, all with robust authentication mechanisms and encryption to ensure your data remains private and protected. SSH is my favorite tool because it provides a secure, efficient, and versatile way to manage and interact with remote systems, making it an essential part of any IT professional's toolkit.
Using socat for Port Exposure vs Port Forwarding
socat is commonly used to make services
reachable when they are bound only to localhost.
Option 1 – Expose a local-only service to the entire machine
sudo socat TCP-LISTEN:8001,fork,bind=0.0.0.0 TCP:127.0.0.1:8000
What it does
- Listens on all network interfaces (
0.0.0.0:8001) - Forwards traffic to a service bound to localhost
(
127.0.0.1:8000) - Requires
sudobecause it exposes the service system-wide
- The application only listens on
127.0.0.1 - You want the service accessible from other machines on the network
- Very common for dev tools, dashboards, scoreboards, internal web apps
This is the most commonly used pattern, because many services bind to localhost by default and just need to be exposed.
Option 2 – Redirect traffic to another host or IP
socat -dd tcp4-listen:8001,fork,reuseaddr tcp4:IP:8000
What it does
- Listens on IPv4 only
- Forwards traffic to another IP or host
-ddenables verbose debug outputreuseaddrallows fast restarts
- Acting as a simple TCP proxy
- Forwarding traffic to a remote machine
- Debugging or tracing TCP connections
This is less common for local services, and more useful when relaying traffic between hosts.
In practice:
Most people use the first command because it exposes a local-only service to the whole machine, which is the typical need.
Most people use the first command because it exposes a local-only service to the whole machine, which is the typical need.
Most commonly used methods of connections (click to expand)
-
Copy Paste - SSH -X option enables X11 forwarding, allowing you to run graphical applications on the remote server and have their display output on your local machine.
ssh macpro -X
Needs to set X11Forwarding yes
-
SSH -J option specifies a jump host, allowing you to connect to a remote server through an intermediate server.
ssh -J first-user@IP 2-user@192.168.100.246
-
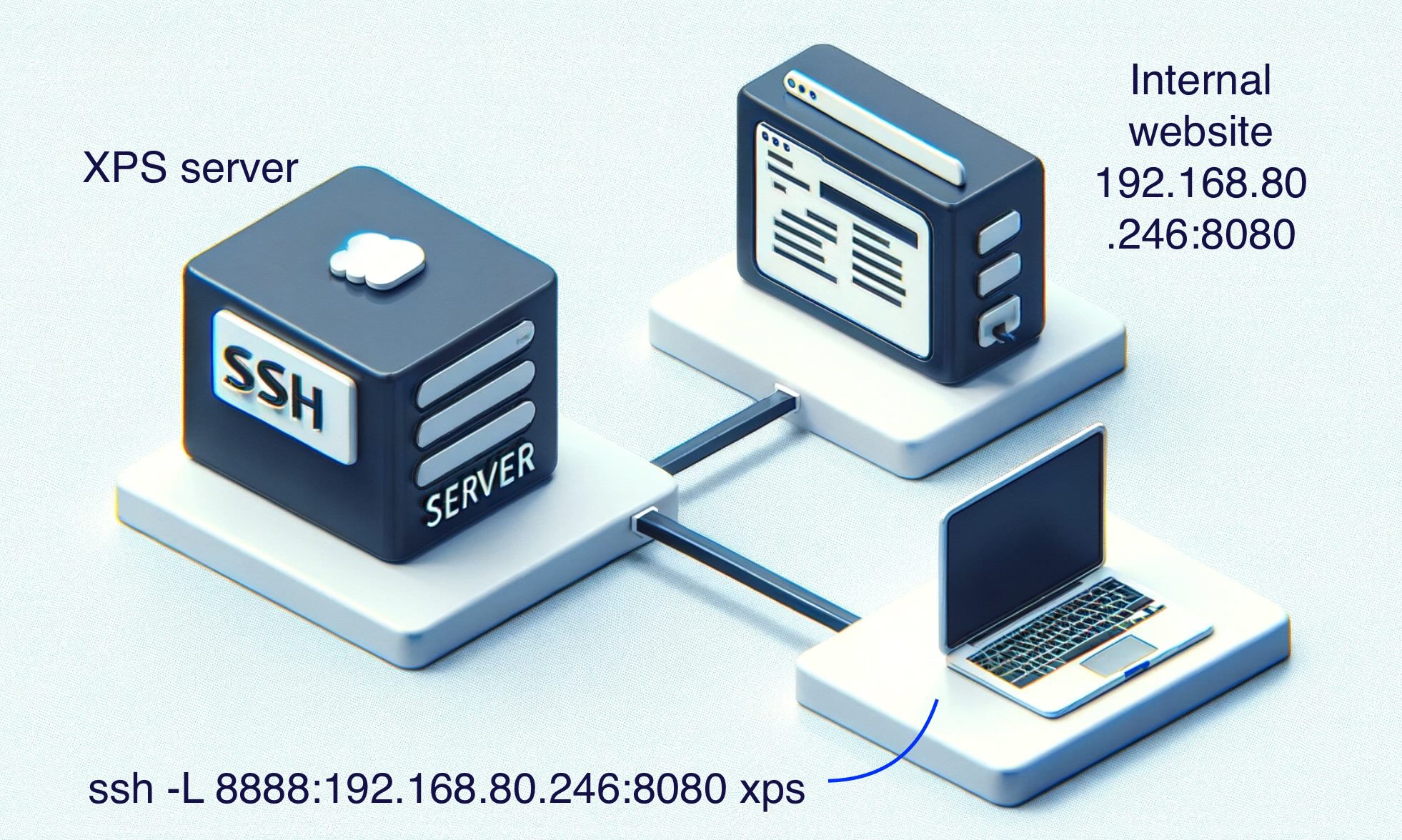
Local Port Forwarding ssh -L
Access to resources that I can't access, like internet Database, RDP
Tambien funciona con socat socat -dd tcp4-listen:8080,fork,reuseaddr tcp4:IP:8080 **** ssh configuration on XPS server needs to have: *** **** AllowTcpForwarding yes **** curl localhost:8888 curl: (7) Failed to connect to localhost port 8888 after 0 ms: Couldn't connect to server ssh -L 8888:192.168.80.246:8080 xps curl localhost:8888 Internal server web flag:as1ds5a6d1a65
-
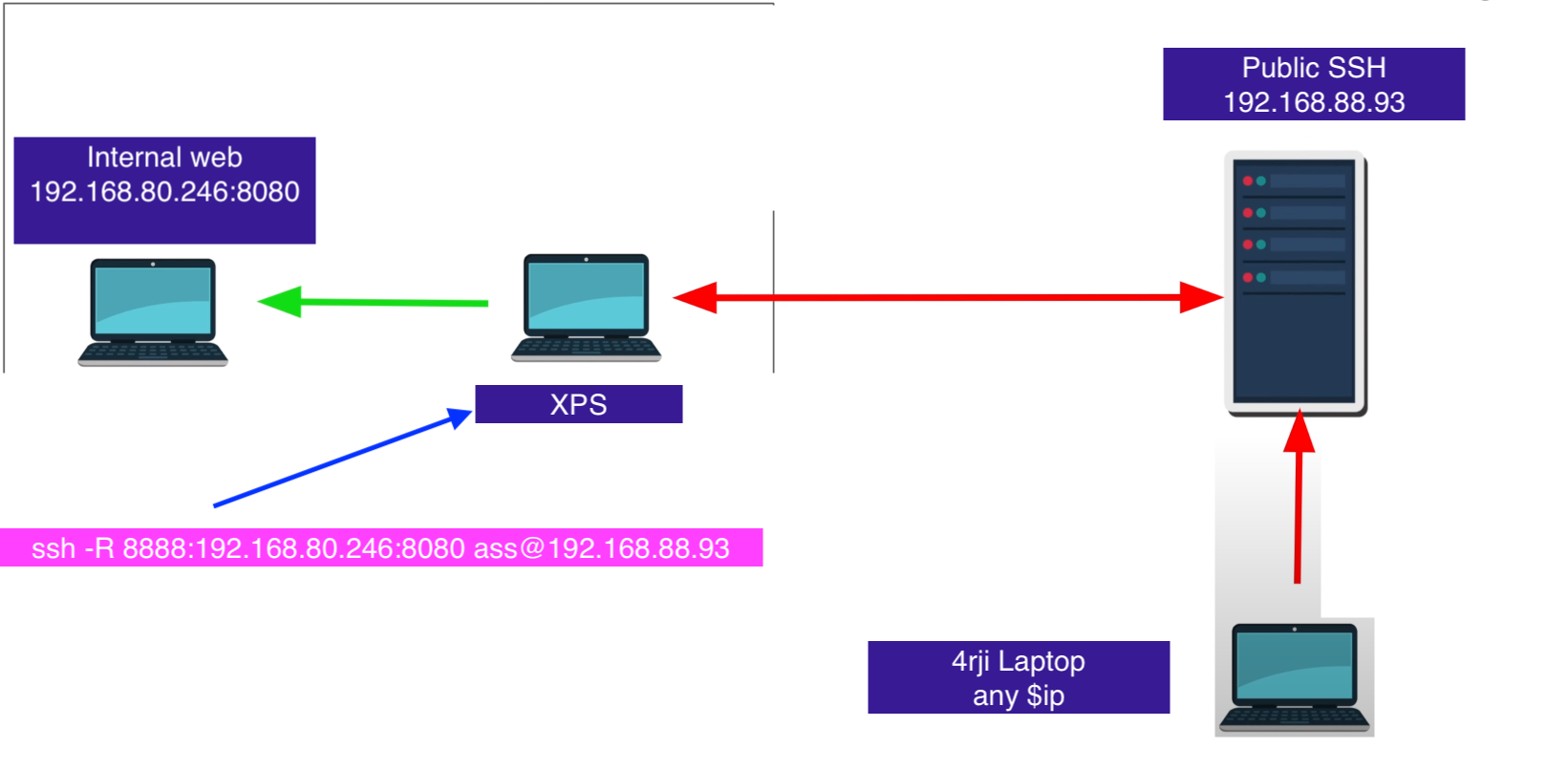
Remote Port Forwarding ssh -R
I want my own server be access to anyone
**** ssh configuration on public server needs to have: *** **** GatewayPorts yes *** ❯ ip r default via 192.168.88.1 dev eth0 192.168.88.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.88.68 ❯ curl http://192.168.88.93:8888/ curl: (7) Failed to connect to 192.168.88.93 port 8888 after 0 ms: Couldn't connect to server #This is execute on XPS ssh -R 8888:192.168.80.246:8080 public@192.168.88.93 curl http://192.168.88.93:8888/ Internal server web flag2:E2lsa3aasd5A
-
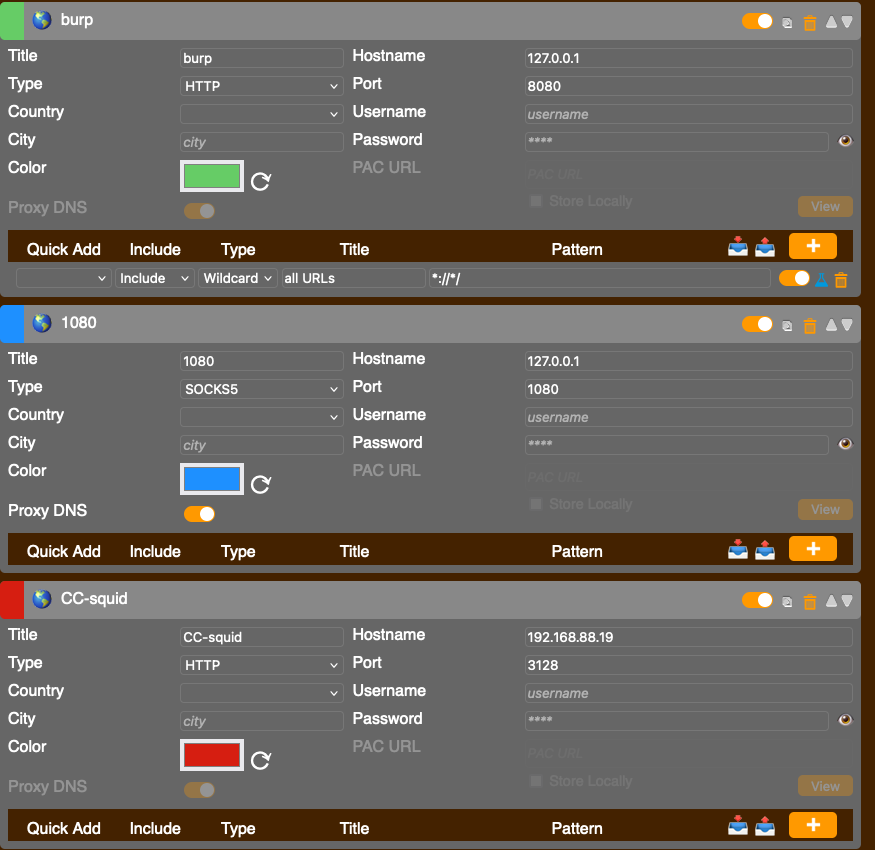
SSH -D 1080 proxy
Setting up foxyproxy
**** ssh configuration on public server needs to have: *** **** AllowTcpForwarding yes *** ssh -D 1080 user@192.168.88.13 -p 2246
-
Sshuttle