Virtualize This! Adventures in the World of Proxmox
Proxmox is a powerful open-source platform for virtualization and container management, designed to deploy, manage, and monitor virtual machines and containers. It combines the features of KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) and LXC (Linux Containers), offering a robust and scalable solution for managing virtual environments. Proxmox allows administrators to efficiently manage VMs, implement high-availability clusters, orchestrate network configurations, and secure deployments with built-in firewall functionalities. Ideal for both small-scale settings and enterprise-level operations, Proxmox provides a flexible and cost-effective approach to data center management.
-
1
Create USB and download the ISO
First, download and create a USB drive using Balena Etcher. Download the Proxmox ISO for servers from https://www.proxmox.com/en/downloads. Then, simply install it like any other operating system. -
2
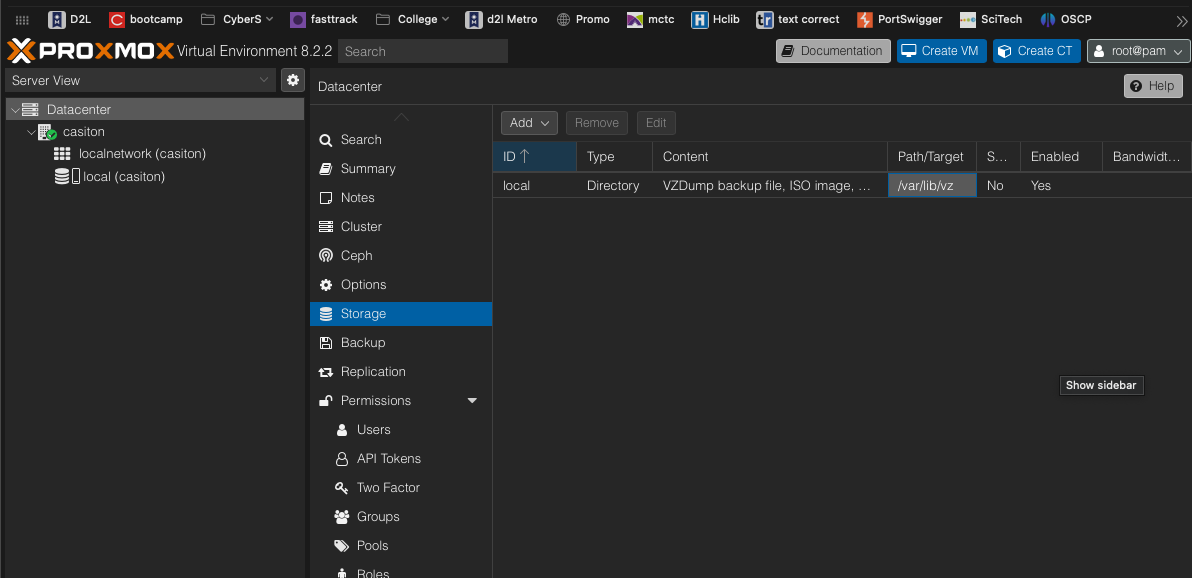
In the Datacenter, delete the local-lvm (Proxmox) so that only one storage option remains, as displayed in the storage image.
Here, the LVM that has been deleted is displayed (ALSO Edit Permissions). -
3
We partition the hard drive.
lvremove /dev/pve/data Do you really want to remove active logical volume pve/data? [y/n]: y Logical volume "data" successfully removed. lvresize -l +100%FREE /dev/pve/root Size of logical volume pve/root changed from 96.00 GiB (24576 extents) to <456.92 GiB (116971 extents). Logical volume pve/root successfully resized. resize2fs /dev/mapper/pve-root resize2fs 1.47.0 (5-Feb-2023) Filesystem at /dev/mapper/pve-root is mounted on /; on-line resizing required old_desc_blocks = 12, new_desc_blocks = 58 The filesystem on /dev/mapper/pve-root is now 119778304 (4k) blocks long. #Done, after the three commands, the hard drive now occupies all the space.
-
4
To prevent the system from going into hibernation or sleep, and also to turn off the screen:
using the script lid uncomment: HandleLidSwitch=ignore HandleLidSwitchExternalPower=ignore HandleLidSwitchDocked=ignore sudo nano /etc/default/grub #Add GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="consoleblank=60" sudo update-grub Generating grub configuration file ... Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-6.8.4-2-pve Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-6.8.4-2-pve Found memtest86+ 64bit EFI image: /boot/memtest86+x64.efi done
- Download
Proxmox web setup
Disk
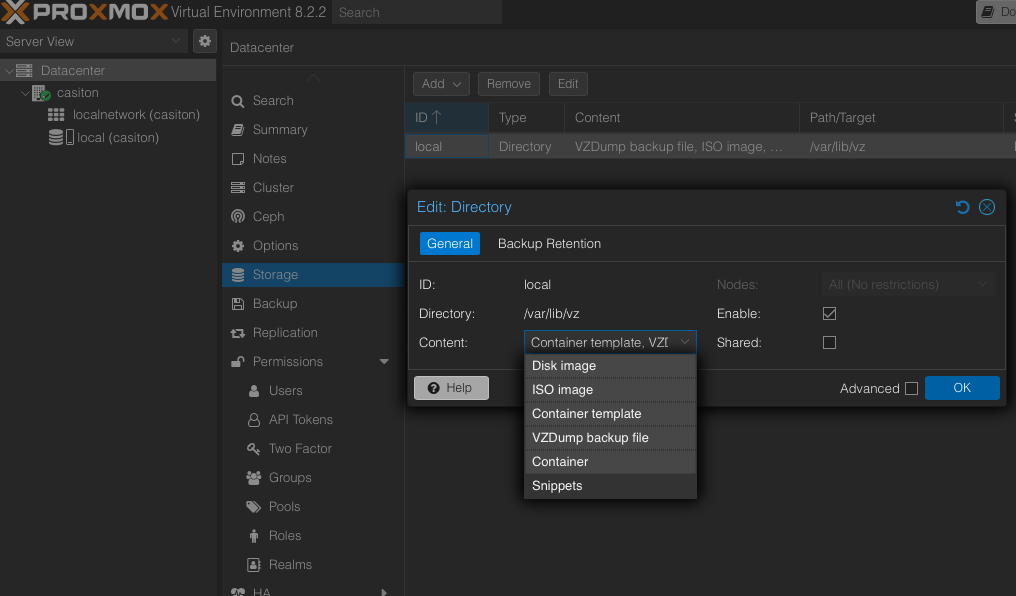
We need to give permission to the hard drive to store VM and Container images.
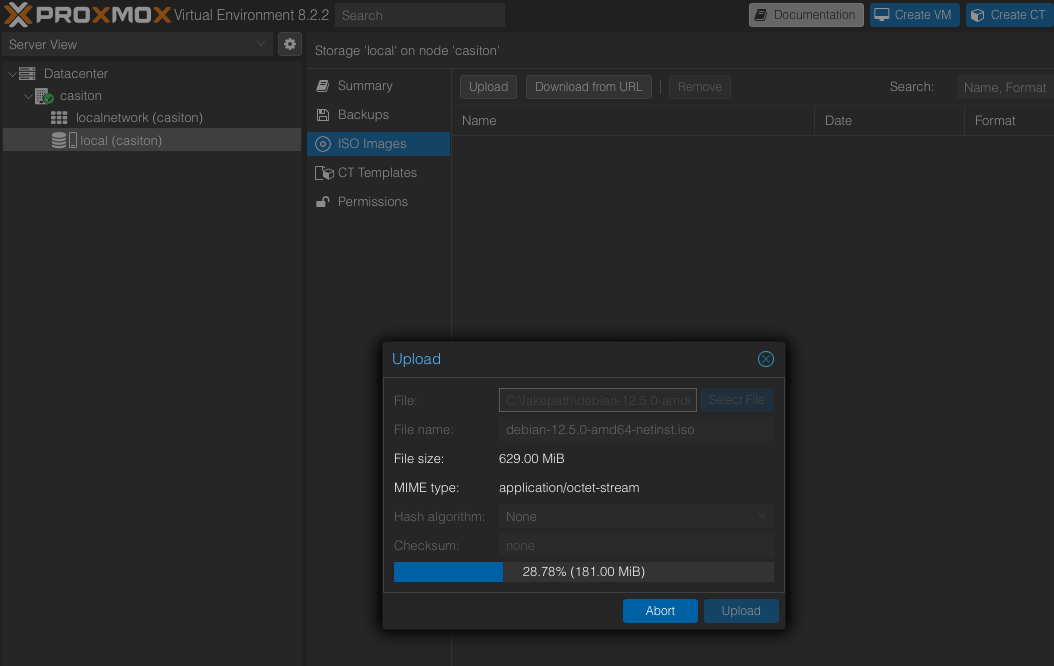
Upload
Upload the ISOs needed to install operating systems.
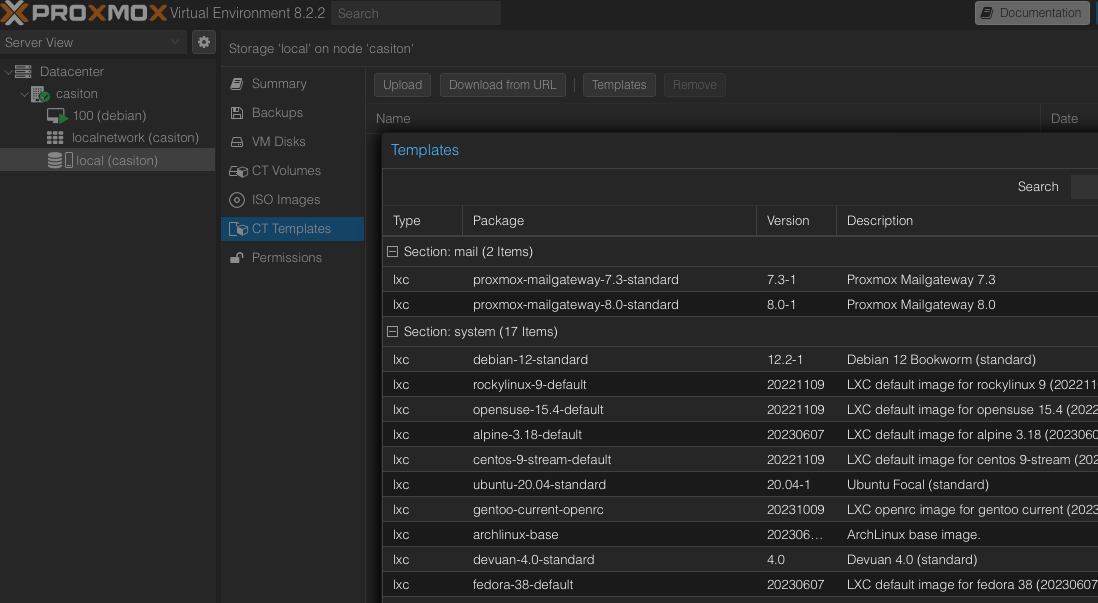
Containers
We can also download container templates for quick deployment of Proxmox CTs (container templates).
VMs
Done, we can now start deploying machines on our new Proxmox.
lid
This is the "lid" script.
#!/bin/bash
# Función para mostrar el mensaje de ayuda y preguntar si desea continuar
show_help_and_confirm() {
echo
echo "El comando que este script ejecuta es:"
echo "sudo nano /etc/systemd/logind.conf"
echo
echo "Presione Enter para continuar o 'c' para salir."
# Preguntar al usuario si desea continuar
read -p "Deseas continuar [c/S] " response
# Convertir la respuesta a minúsculas
response=$(echo "$response" | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')
# Si la respuesta es 'c', salir del script
if [ "$response" == "c" ]; then
echo "Saliendo del script."
exit 0
fi
}
# Verificar si se pasó el argumento -h
if [ "$1" == "-h" ]; then
show_help_and_confirm
fi
sudo nano /etc/systemd/logind.conf
echo "Restart the service now? (Press S for yes, Enter for no)"
read -k1 input
if [[ $input == "S" || $input == "s" ]]; then
sudo systemctl restart systemd-logind
echo "systemd-logind service restarted."
else
echo "You chose not to restart the service. Changes will take effect on next reboot."
fi
Nvidia Installation
This script is designed to configure a Linux system for using VFIO (Virtual Function I/O), which allows you to pass through hardware devices, such as GPUs, directly to virtual machines. This setup is particularly useful for high-performance tasks like gaming or GPU-intensive applications in a VM.
#!/bin/bash
#for kali I follow this after I run this scritp and reboot:
#sudo nano /etc/default/grub
#sudo update-grub
#sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
#sudo apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
#sudo apt install linux-image-amd64
#sudo apt install linux-headers-amd64
#sudo apt install linux-headers-generic
#wget https://uk.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86_64/555.42.02/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-555.42.02.run
# Ruta del archivo de configuración de GRUB
GRUB_CONFIG="/etc/default/grub"
# Backup del archivo de configuración de GRUB antes de modificarlo
cp $GRUB_CONFIG $GRUB_CONFIG.bak
# Comenta la línea existente y añade la nueva configuración debajo
sed -i '/GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=/c\#&\nGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet intel_iommu=on"' $GRUB_CONFIG
# Actualizar GRUB
update-grub
# Backup de los archivos de configuración antes de modificarlos
cp /etc/modules /etc/modules.bak
# Verificar y hacer backup de los archivos de configuración específicos si existen
[[ -f /etc/modprobe.d/iommu_unsafe_interrupts.conf ]] && cp /etc/modprobe.d/iommu_unsafe_interrupts.conf /etc/modprobe.d/iommu_unsafe_interrupts.conf.bak
[[ -f /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf ]] && cp /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf.bak
[[ -f /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf ]] && cp /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf.bak
[[ -f /etc/modprobe.d/vfio.conf ]] && cp /etc/modprobe.d/vfio.conf /etc/modprobe.d/vfio.conf.bak
# Añadir módulos VFIO al archivo de módulos
echo "vfio" >> /etc/modules
echo "vfio_iommu_type1" >> /etc/modules
echo "vfio_pci" >> /etc/modules
echo "vfio_virqfd" >> /etc/modules
# Crear o modificar archivos de configuración con los valores necesarios
echo "options vfio_iommu_type1 allow_unsafe_interrupts=1" > /etc/modprobe.d/iommu_unsafe_interrupts.conf
echo "options kvm ignore_msrs=1" > /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf
echo "blacklist radeon" > /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
echo "blacklist nouveau" >> /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
echo "blacklist nvidia" >> /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
echo "options vfio-pci ids=10de:2484,10de:228b,10de:0ffd,10de:0e1b disable_vga=1" > /etc/modprobe.d/vfio.conf
# Actualizar initramfs
update-initramfs -u
echo -e "\n\033[1;32m_________________________________________________________\033[0m\n"
echo "instructions inside this script for kali"
echo -e "\n\033[1;32m_________________________________________________________\033[0m\n"
#1b:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GA104 [GeForce RTX 3070] (rev a1) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
#1b:00.0 0300: 10de:2484 (rev a1)
#" con lspci -v buscamos
#04:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GA104 [GeForce RTX 3070] (rev a1) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
#03:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation GK107 [NVS 510] (rev a1) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])"
#de ahi tomamos y ponemos:
#lspci -n -s 04:00
#04:00.0 0300: 10de:2484 (rev a1)
#04:00.1 0403: 10de:228b (rev a1)
#lspci -n -s 03:00
#03:00.0 0300: 10de:0ffd (rev a1)
#03:00.1 0403: 10de:0e1b (rev a1)
#para crear las lineas:
#options vfio-pci ids=10de:2484,10de:228b,10de:0ffd,10de:0e1b disable_vga=1
#https://youtu.be/X_VwQpJSXIQ?si=nPfJwXS8sX9CZ9iWFor kali
To install the nvidia in kali
#!/bin/bash
# Download the NVIDIA driver
echo "Downloading the NVIDIA driver..."
wget https://uk.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86_64/555.42.02/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-555.42.02.run
# Ensure the script is executable
chmod +x NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-555.42.02.run
# Disable the nouveau module
echo "Disabling the nouveau module..."
echo "blacklist nouveau" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf > /dev/null
echo "options nouveau modeset=0" | sudo tee -a /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf > /dev/null
# Install development tools and headers for the current kernel
echo "Installing development tools and kernel headers..."
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y build-essential linux-headers-$(uname -r)
# Update initramfs
echo "Updating initramfs..."
sudo update-initramfs -u
# Final message
echo "Please reboot the machine to apply changes."
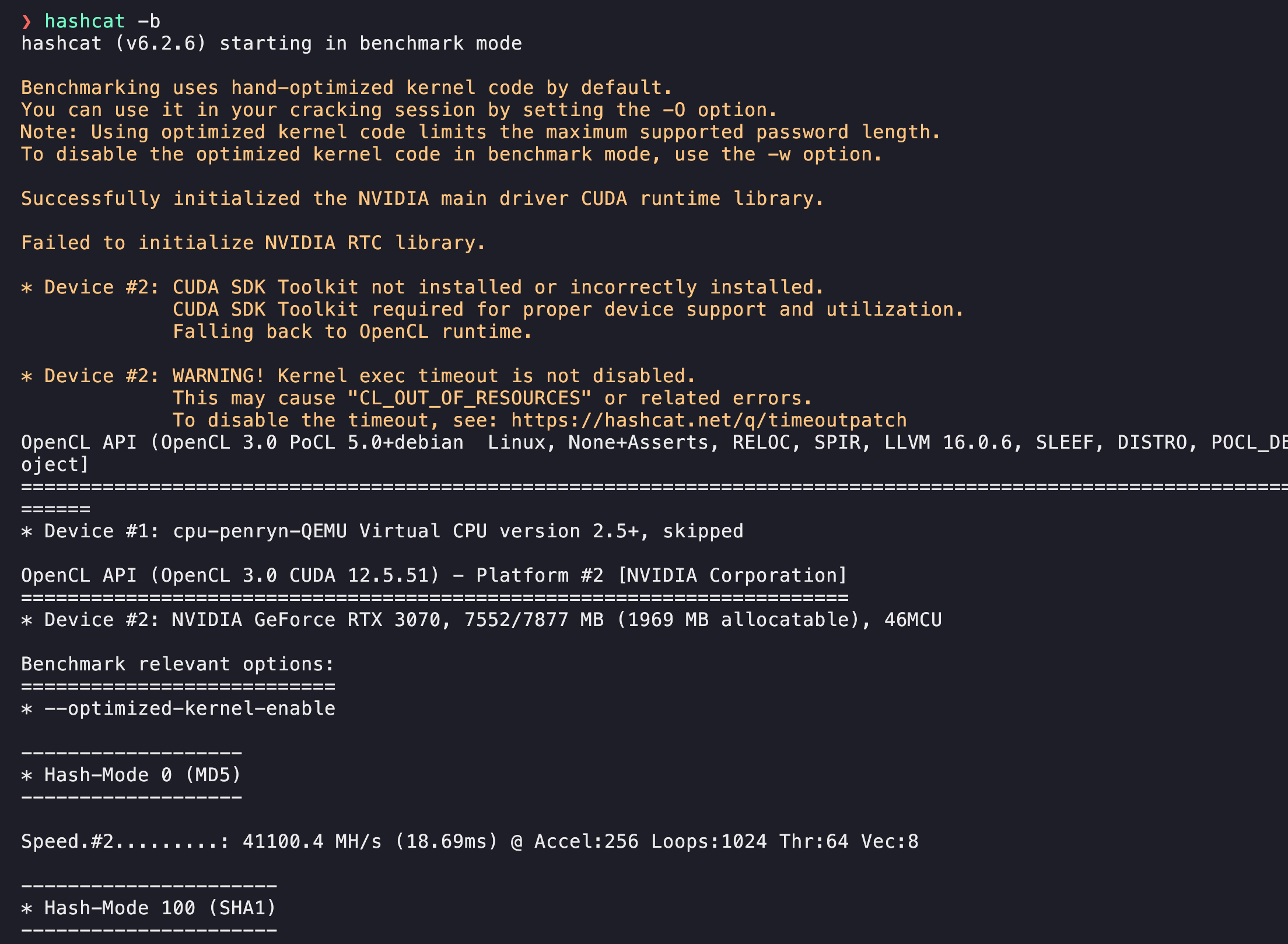
Kali using NVIDIA with hashcat
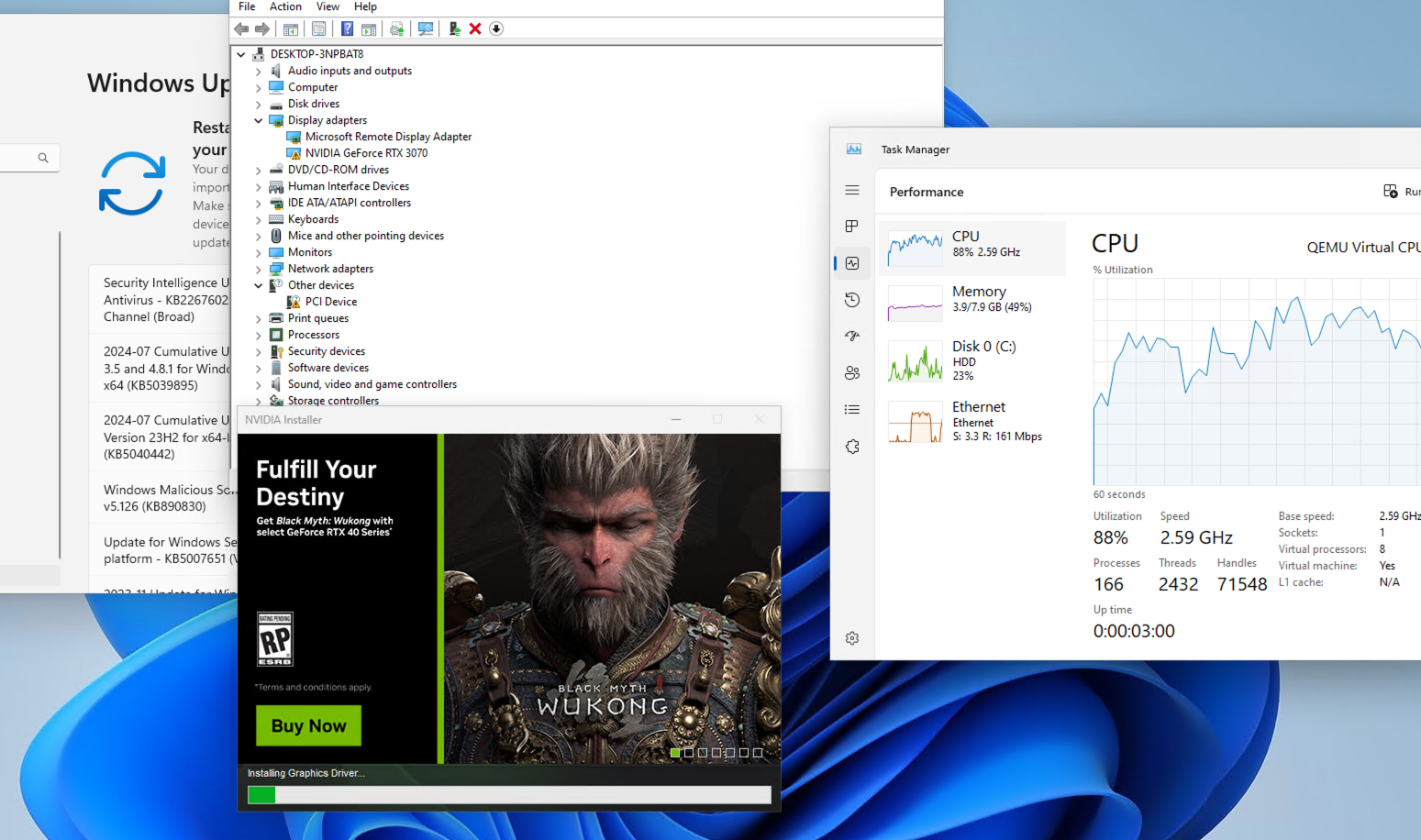
Windows after adding PCI Nvidia
Terminal qm activation
Steps
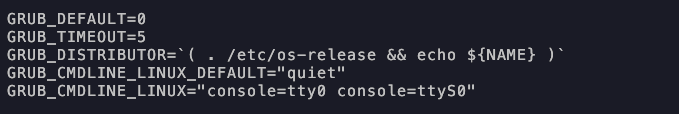
Edit grub
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
sudo systemctl enable serial-getty@ttyS0.servicesudo systemctl start serial-getty@ttyS0.service
sudo update-grub
sudo shutdown -h now
Set serial
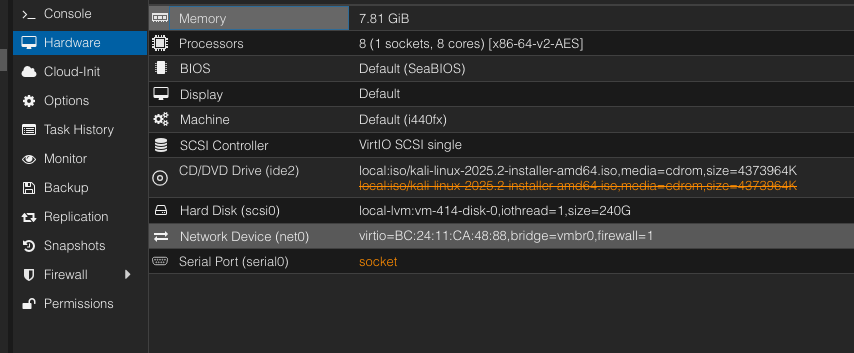
serial port with VM shutdown
log into proxmox server and execute:qm set 414 -serial0 socket
#changa 414 for the VM id
Start VM
Make sure the Serial port is not highlighted red
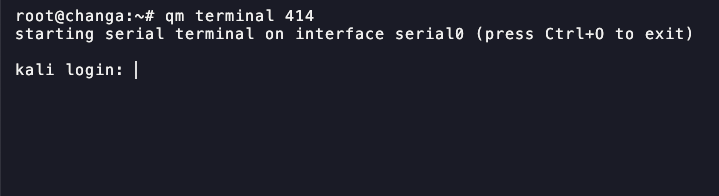
Log into VM
From Proxmox Cli execute: qm terminal VM-ID
Adding Second HD and ISOS
Steps
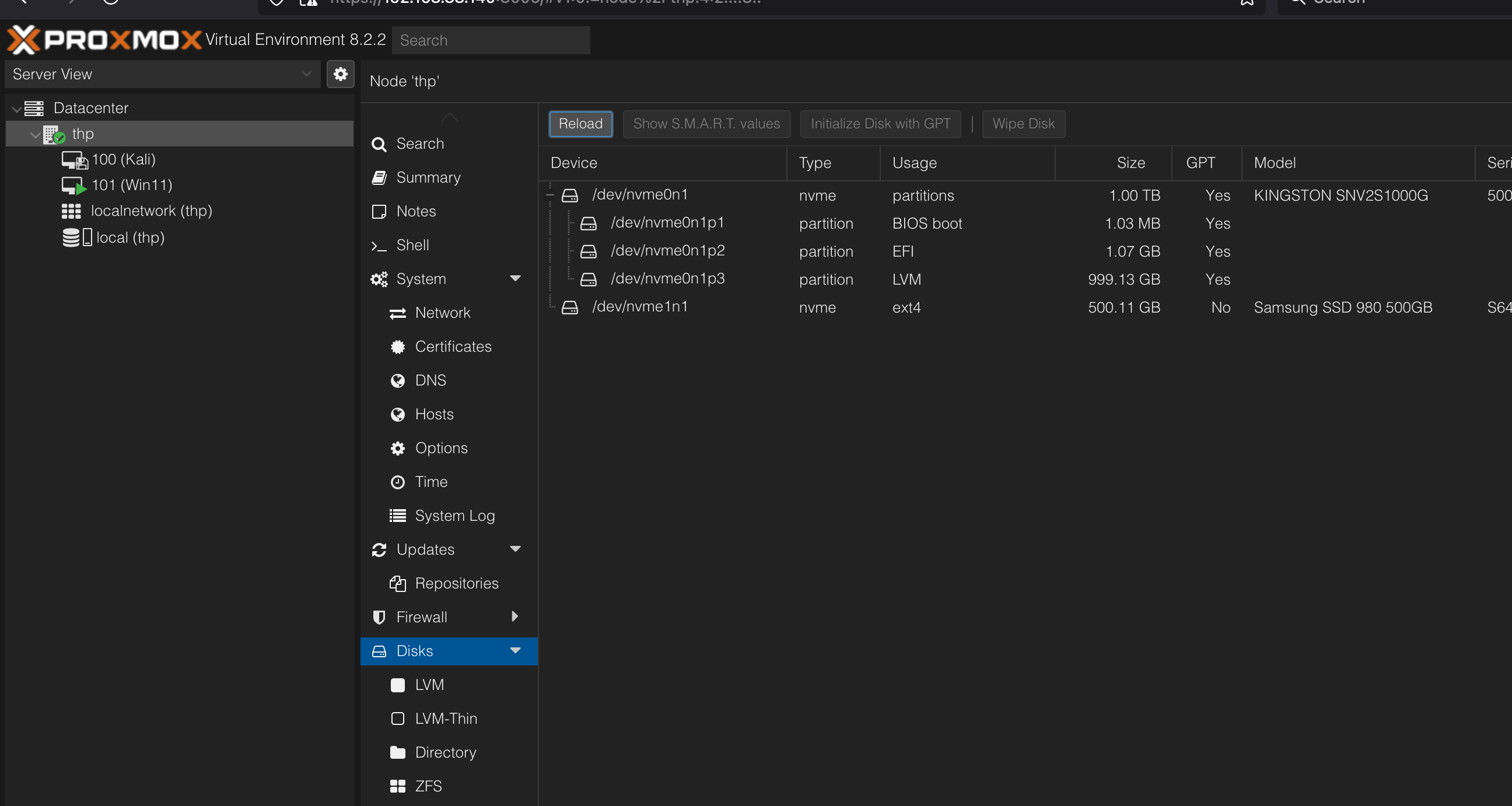
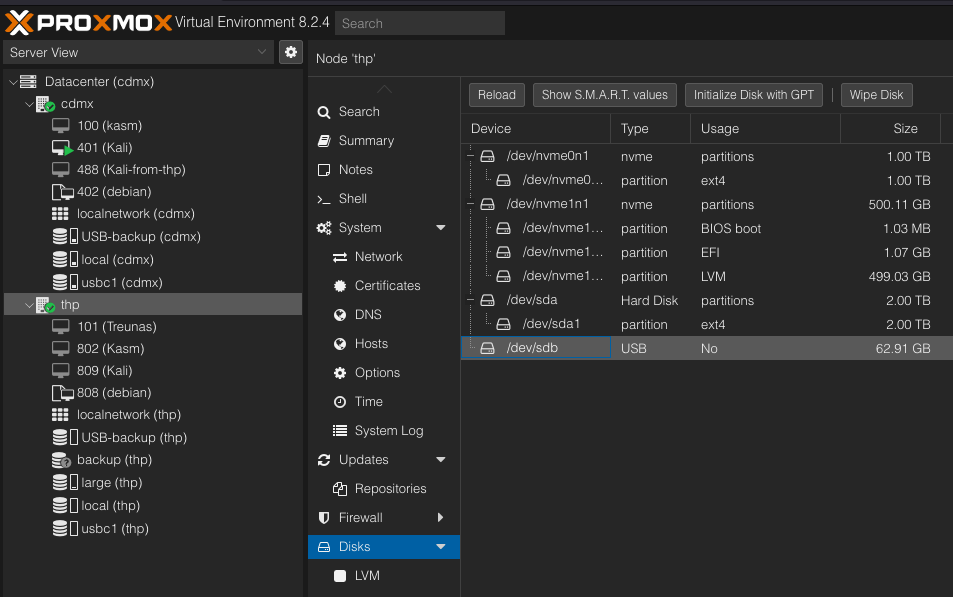
Wipe and GPT
Wipe Disk and then Initialize Disk with GPT
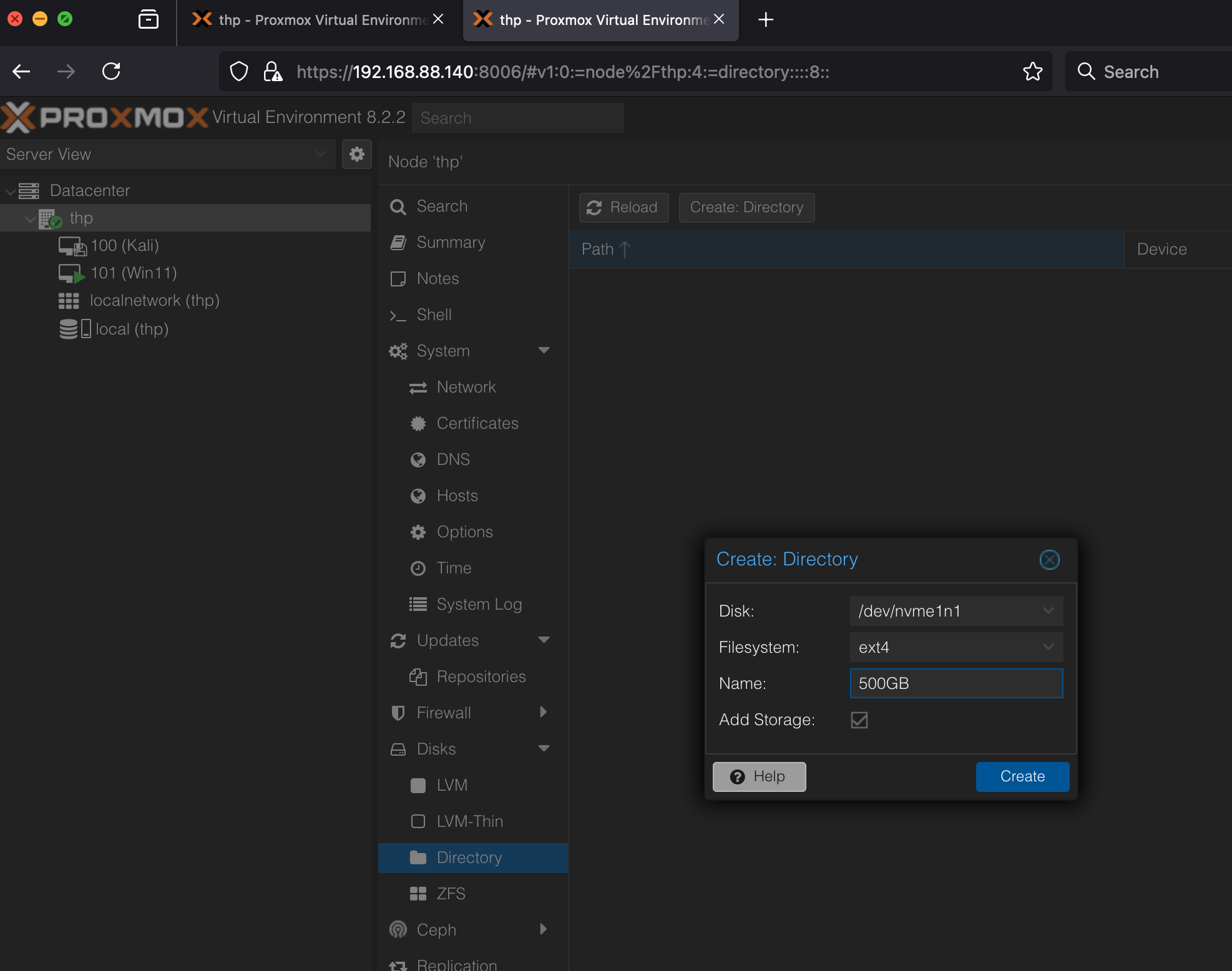
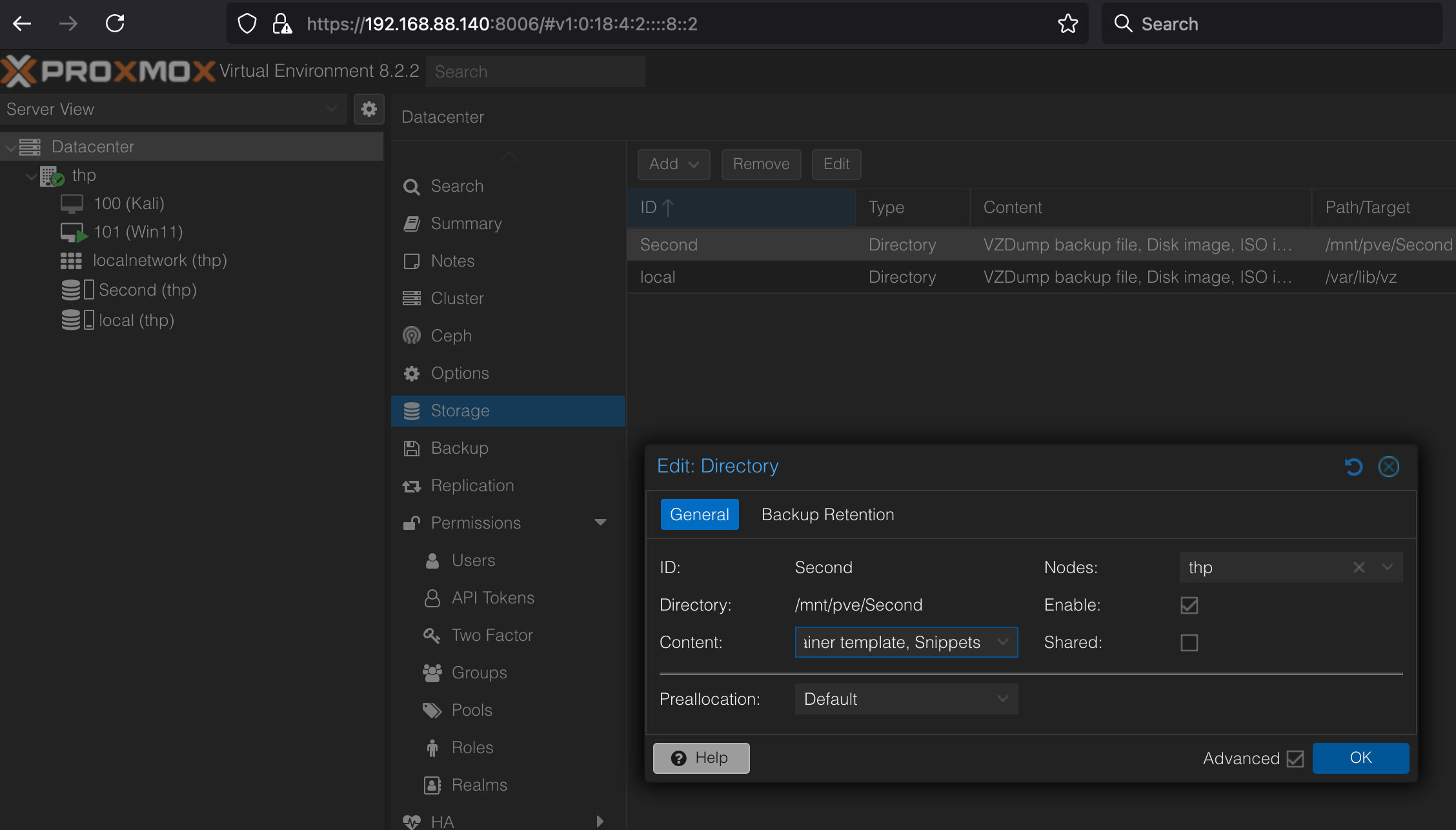
Directory
Create the directory
Permissions
Just in case we need to update the permissions
Isos
ISOs can be moved from the terminal
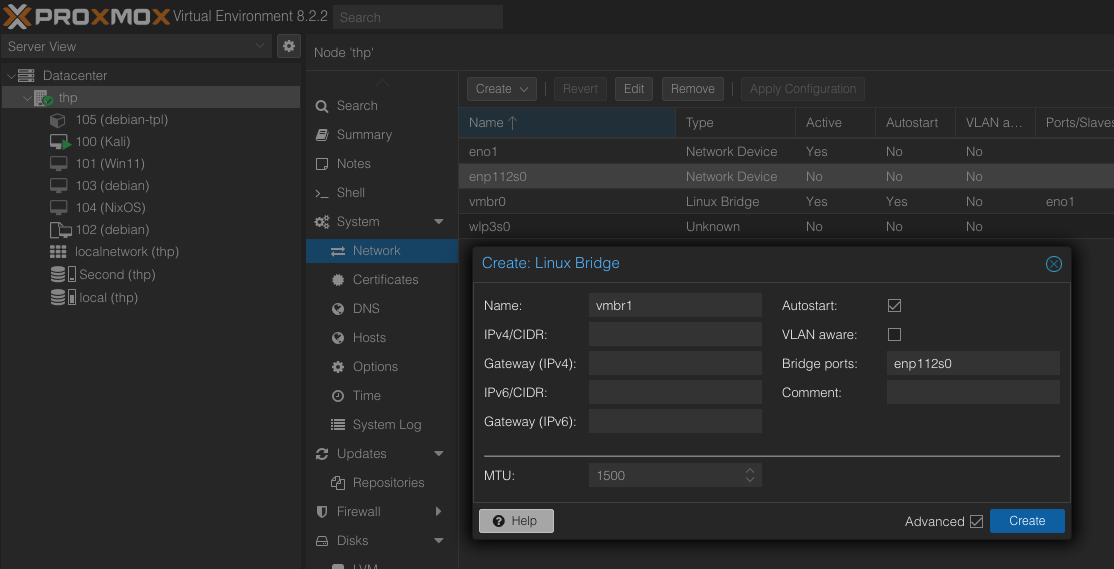
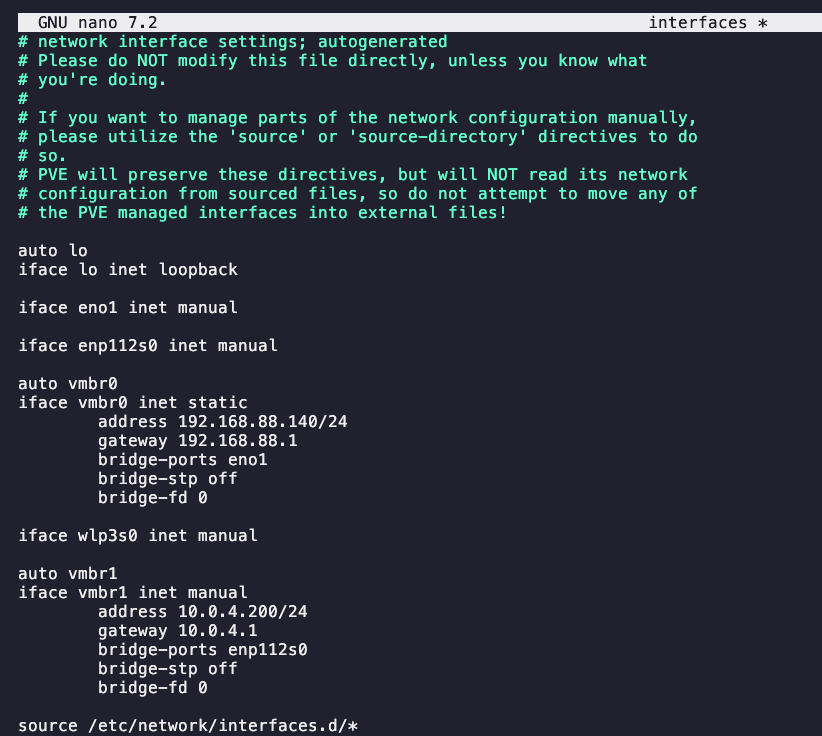
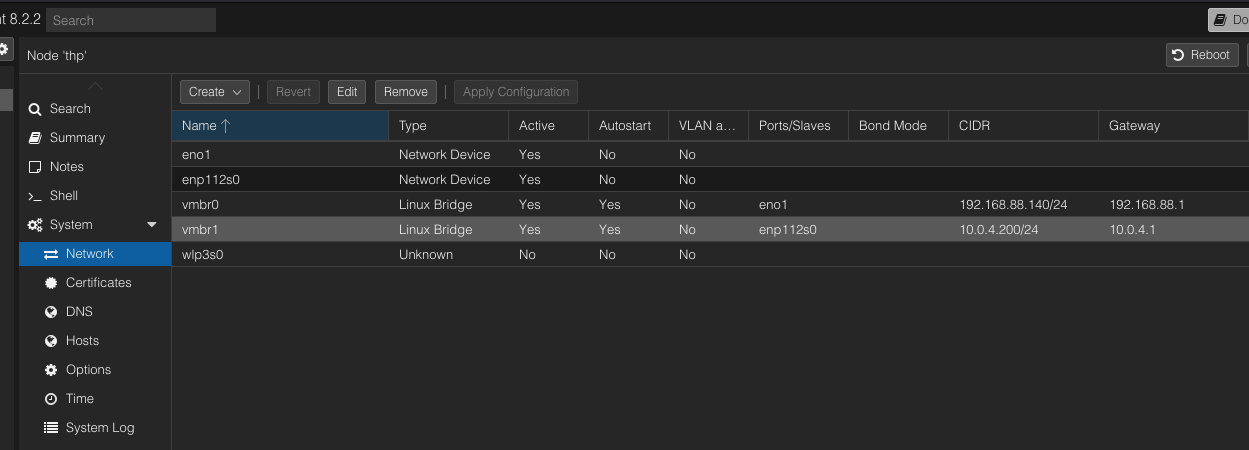
Adding ethernet interfaces
Create the new bridge just
Just add the name of the interface to active, put the name on bridge ports
Click Apply the configuration
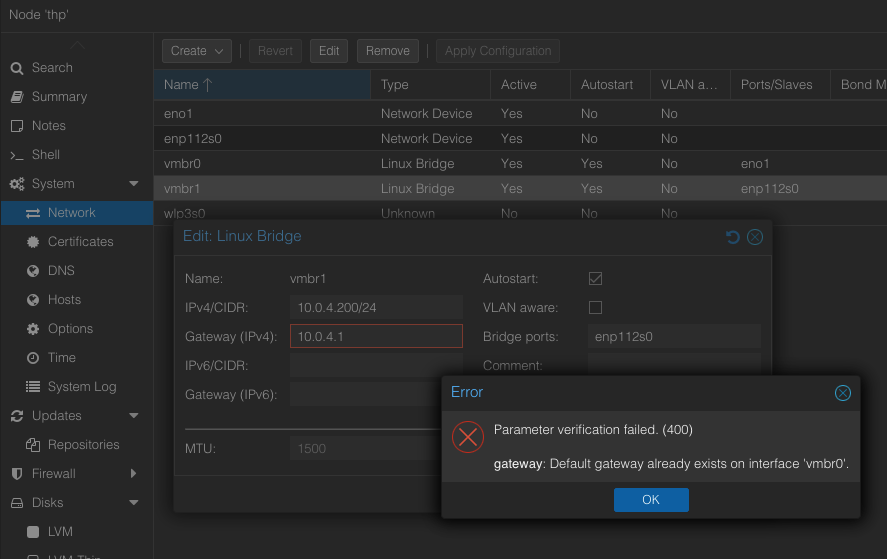
Assign IP
If you get an error assigning the IP, use CLI
Assign IP CLI
Just add address and gateway lines to the file /etc/network/interfaces
Good idea to make a copy of the file before editing
Its done
Now the network is avaiable to assign to any VM
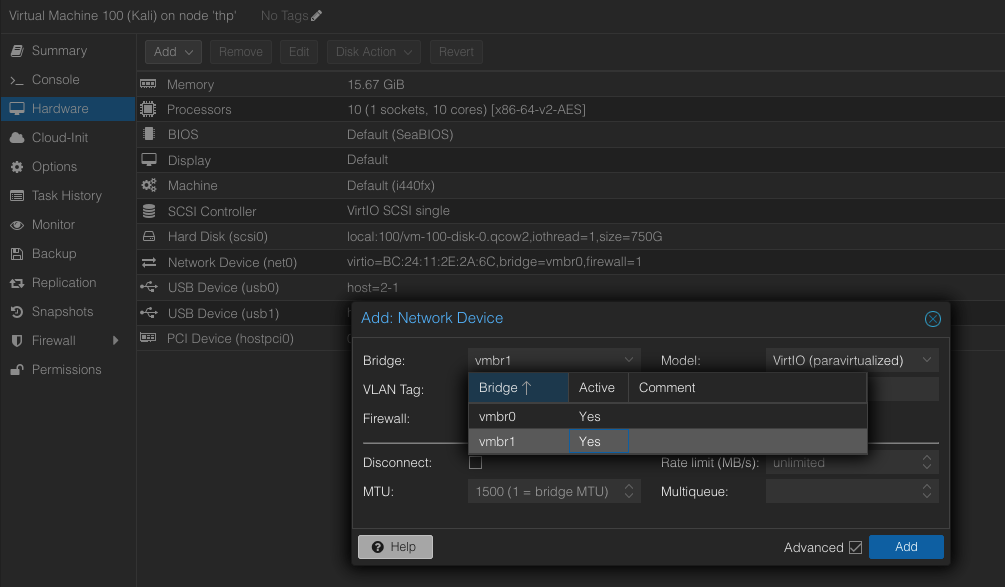
Adding new Network
Here I am adding the new interfaces which is a VPN network on Unifi
Backup
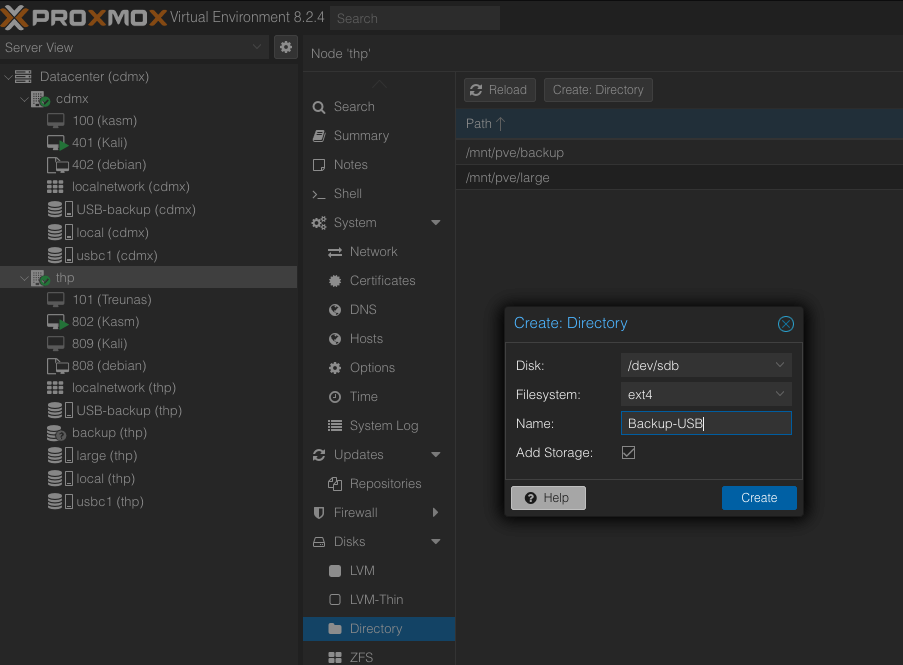
Insert USB and wipe it
Wipe and Initialize
Add Directory
Add all the content and mount the directory
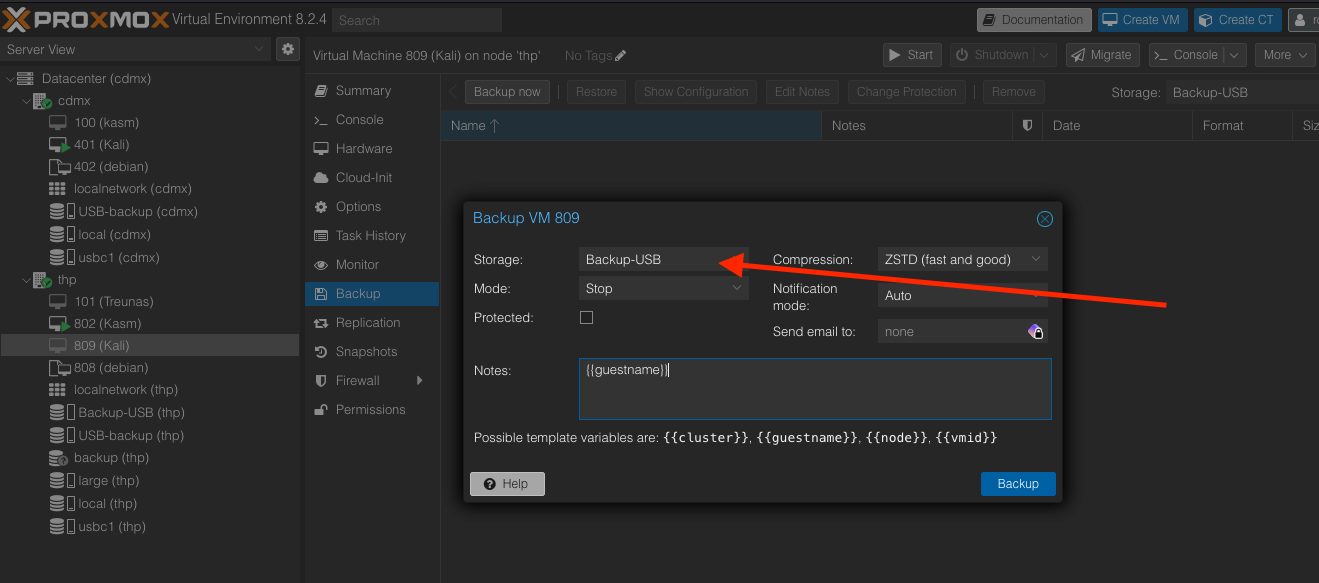
Back up VM
Back up the vm in the new directory, USB, with STOP mode.
Make sure the USB-driver is select.
Umount
After backup is done, unmount the USB
root@thp:~# sudo umount /mnt/pve/Backup-USBRestore
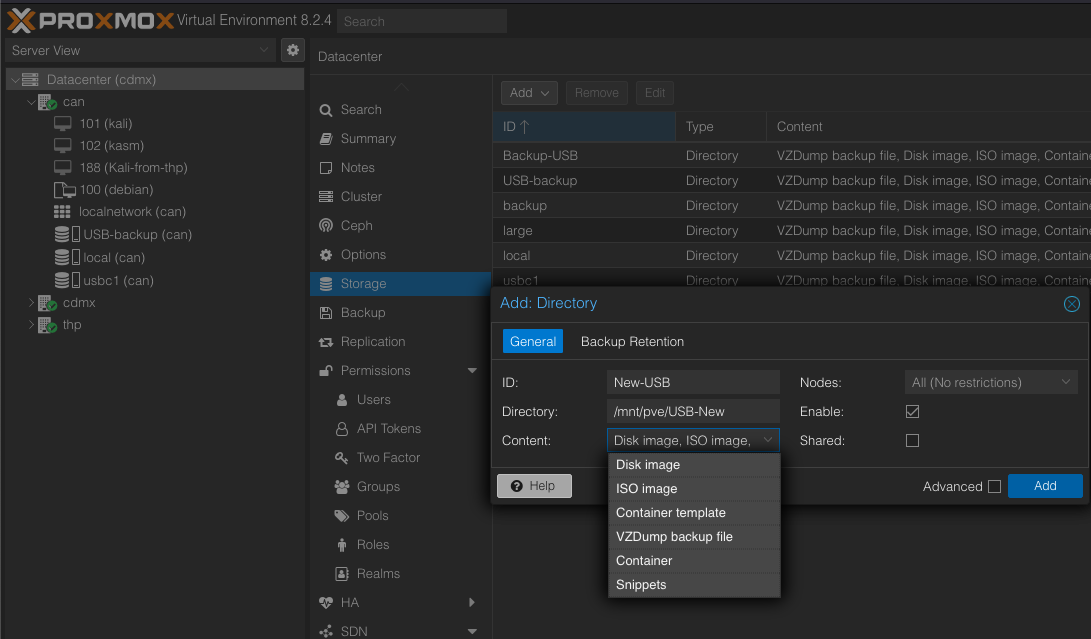
Insert USB and mount
Go to shell and create a new folder
mkdir /mnt/pve/USB-New
#find the USB
❯ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
sda 8:0 0 931.5G 0 disk
└─sda1 8:1 0 931.5G 0 part /mnt/pve/Samsung
sdb 8:16 1 58.6G 0 disk
└─sdb1 8:17 1 58.6G 0 part
#Mount the usb
sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/pve/USB-New
❯ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
sda 8:0 0 931.5G 0 disk
└─sda1 8:1 0 931.5G 0 part /mnt/pve/Samsung
sdb 8:16 1 58.6G 0 disk
└─sdb1 8:17 1 58.6G 0 part /mnt/pve/USB-New
nvme0n1 259:0 0 953.9G 0 disk Add storage USB
Also add all the content.
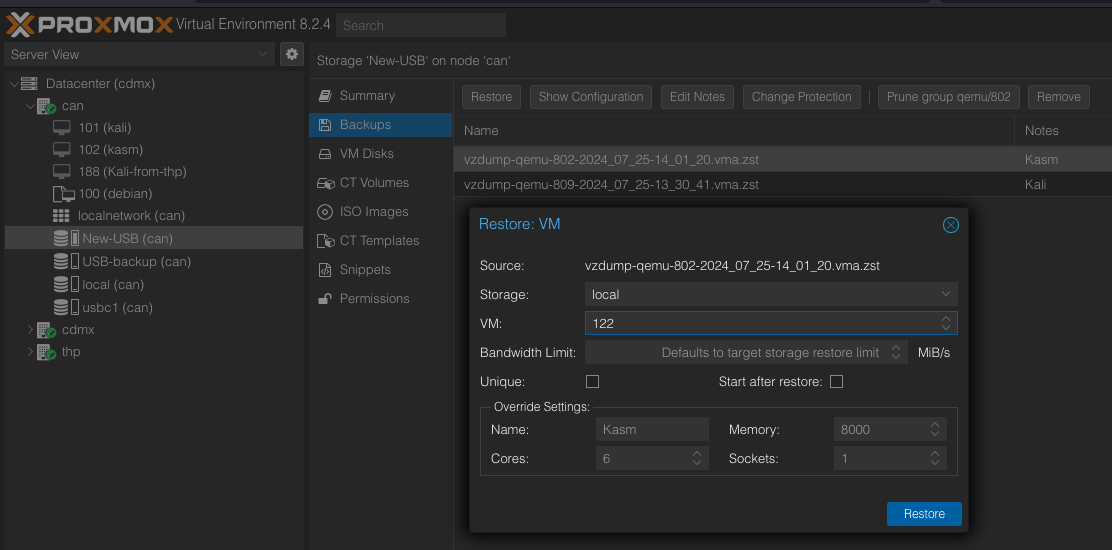
Restore VMs
Go to the new storage created and restore the VMs
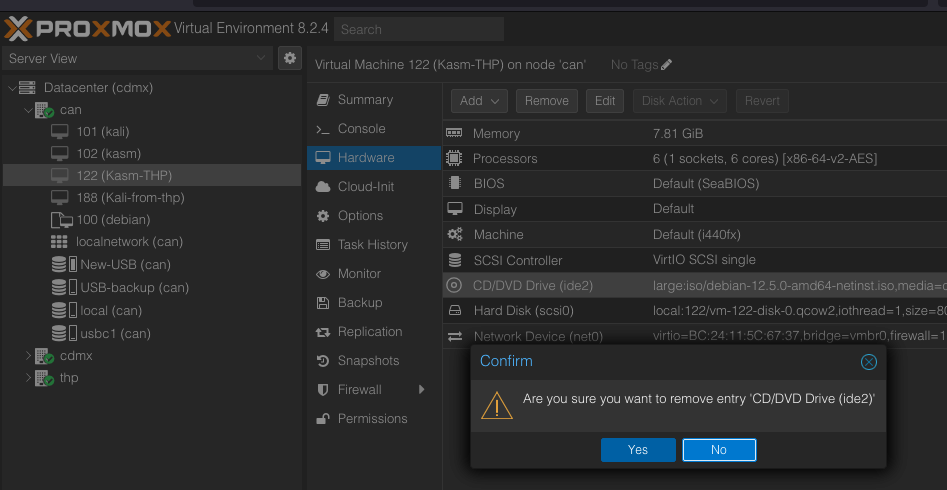
Remove hardware
Remove any hardward not available.
Ready
Now you can see the VM created.
Dont forget to unmount the USB: sudo umount /mnt/pve/USB-New
Nodes
Multiple nodes (servers)
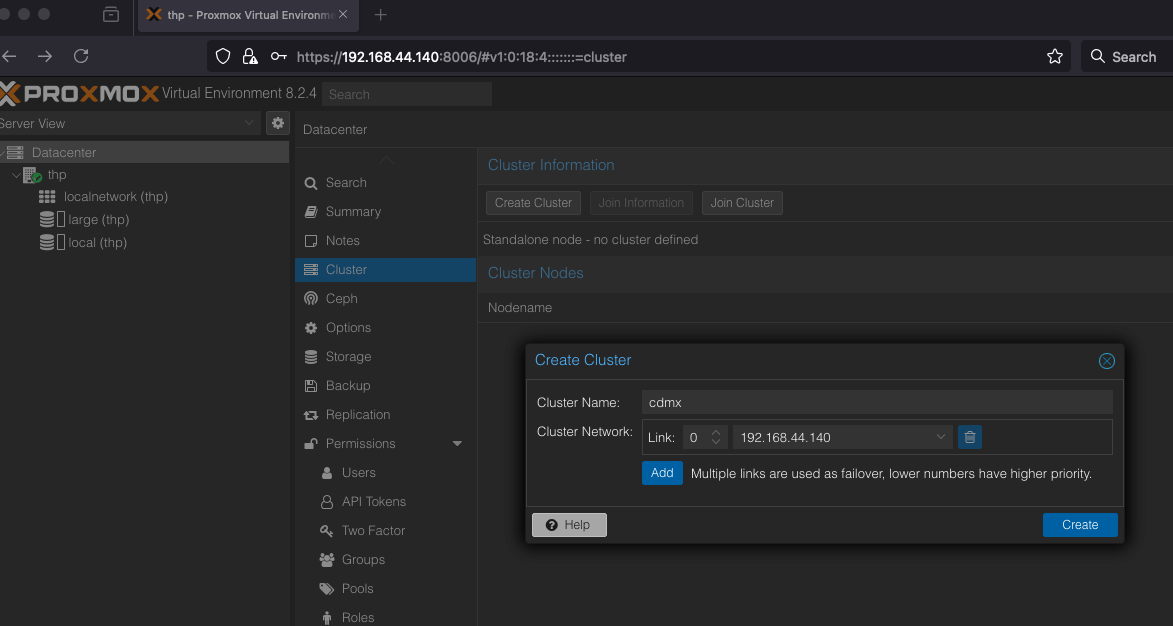
Create Cluster
On the server host create a cluster
Stop VMs and move config files
Then move the configuration VMs files somewhere else
cd /etc/pve/nodes/can/qemu-server
#Move files to home
mv * ~
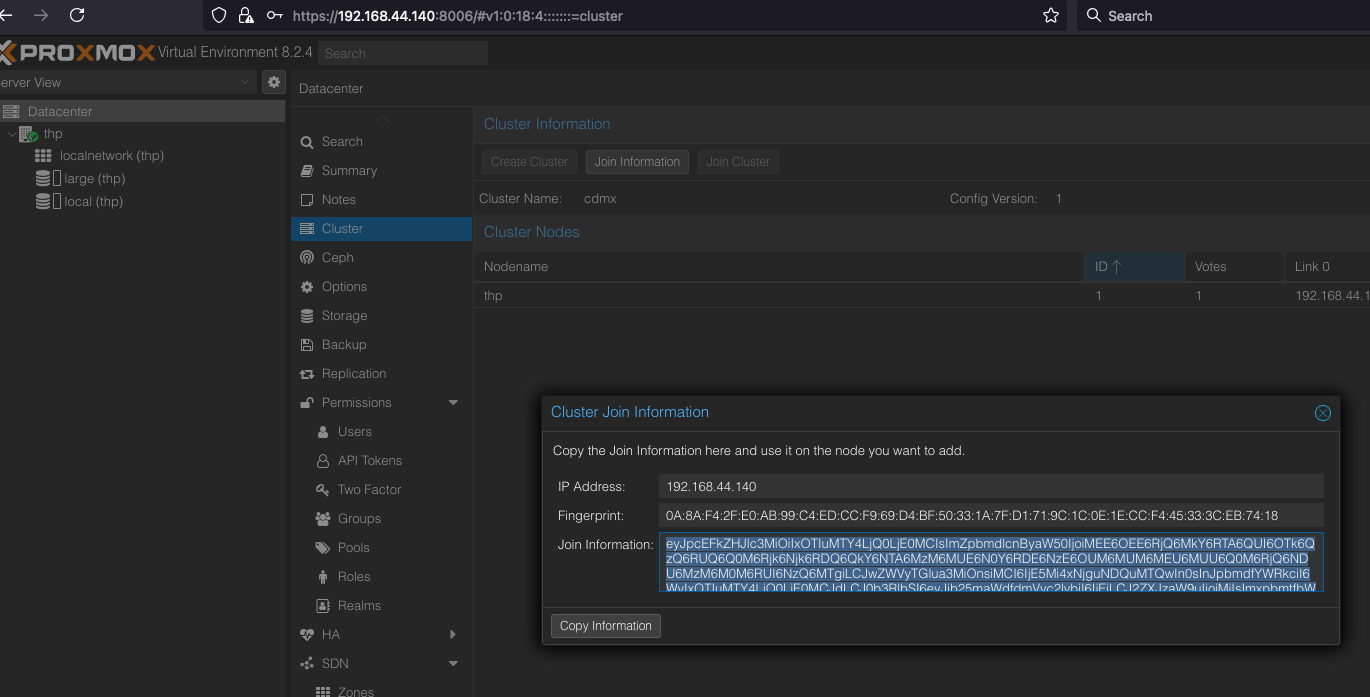
Info
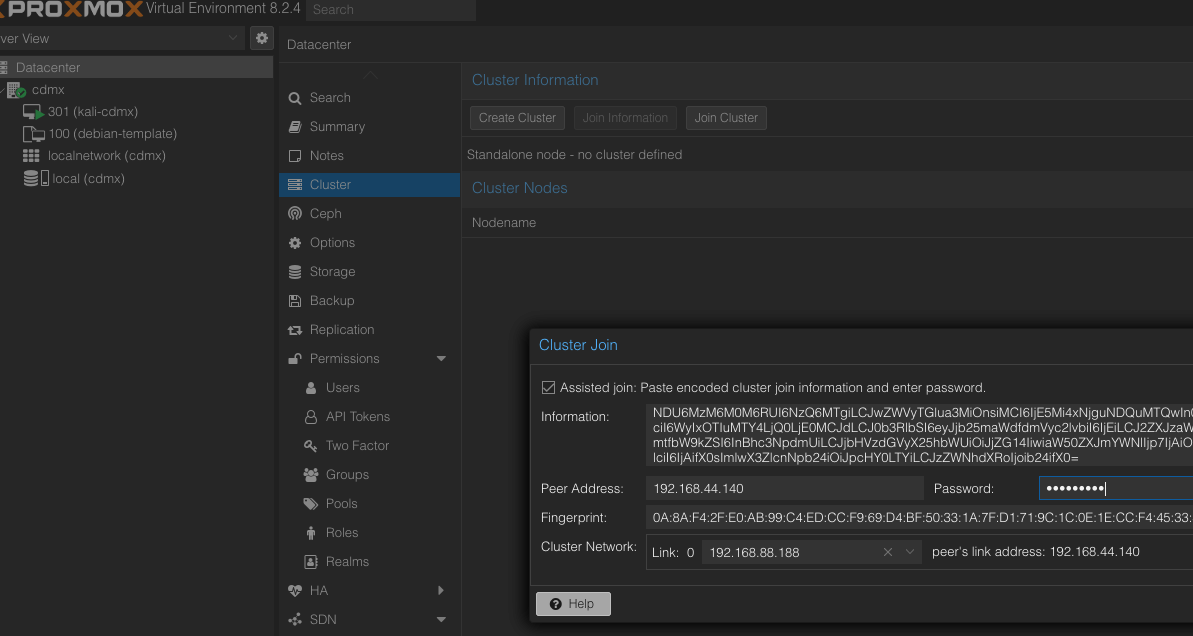
Copy join information
Join server
Join the servers
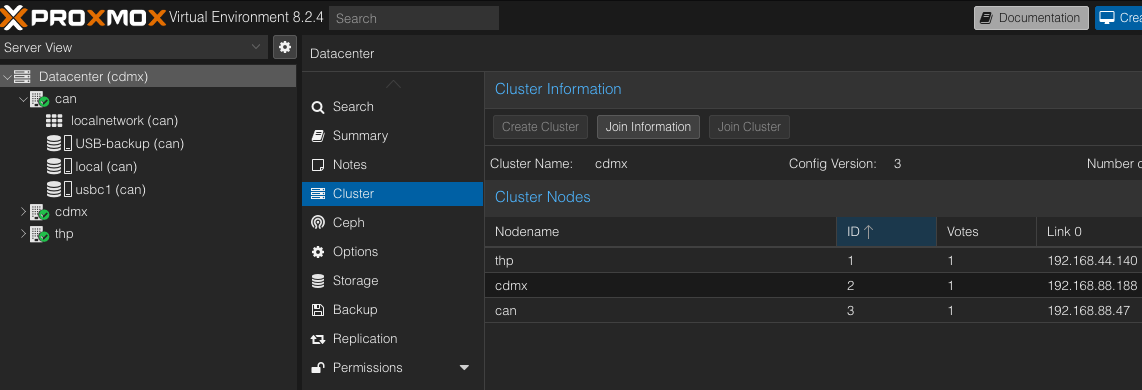
Servers
Now all the Nodes are connected.
Restore VMs
Put the files back to the directory
❯ mv * /etc/pve/nodes/can/qemu-server
mv: cannot create regular file '/etc/pve/nodes/can/qemu-server/100.conf': File exists
mv: cannot create regular file '/etc/pve/nodes/can/qemu-server/101.conf': File exists
❯ cd -
/etc/pve/nodes/can/qemu-server
❯ ls
102.conf 188.confSince we have VMs with same numbers, we need to changes the configuration files.
Ready, enjoy.