Unleash Productivity, Anywhere, Anytime!
Kasm Workspaces is a cutting-edge container streaming platform that revolutionizes the way you manage and access your applications and desktops. It provides a secure, scalable, and user-friendly environment that allows you to deploy and manage workspaces with ease, enhancing productivity while maintaining robust security protocols. Whether you're working from home or managing a team remotely, Kasm makes it seamless to connect and collaborate effectively.
kasminst
This Bash script is designed to automate the setup of a development environment by installing essential packages such as Docker and Docker Compose across various Linux distributions including Debian, Ubuntu, Kali, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, and Arch Linux. It first checks if these packages are installed, and if not, proceeds to install them using the package manager appropriate for the detected OS. Additionally, the script configures swap space based on the user's input for desired RAM, and ensures this swap file is activated at boot. Finally, the script downloads and installs Kasm, a software used for creating secure, containerized workspaces, thus streamlining the setup process for a development or testing environment.
kasminst dpkg-query: no packages found matching docker.io Instalando el paquete docker.io... Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-g
How much GB of RAM do you want (4, 6, 8...) : 8 8192+0 records in 8192+0 records out
A copy of the End User License Agreement is located at: /tmp/kasm_release/licenses/LICENSE.txt I have read and accept End User License Agreement (y/n)? y Get:1 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security InRelease [48.0 kB] Hit:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm InRelease
After installing the script, we access the website using the credentials displayed at the end of the installation.
Installation Complete Kasm UI Login Credentials ------------------------------------ username: admin@kasm.local password: xtPToPSwDzS10 ------------------------------------ username: user@kasm.local password: 7HLvvh7UXs5UW ------------------------------------
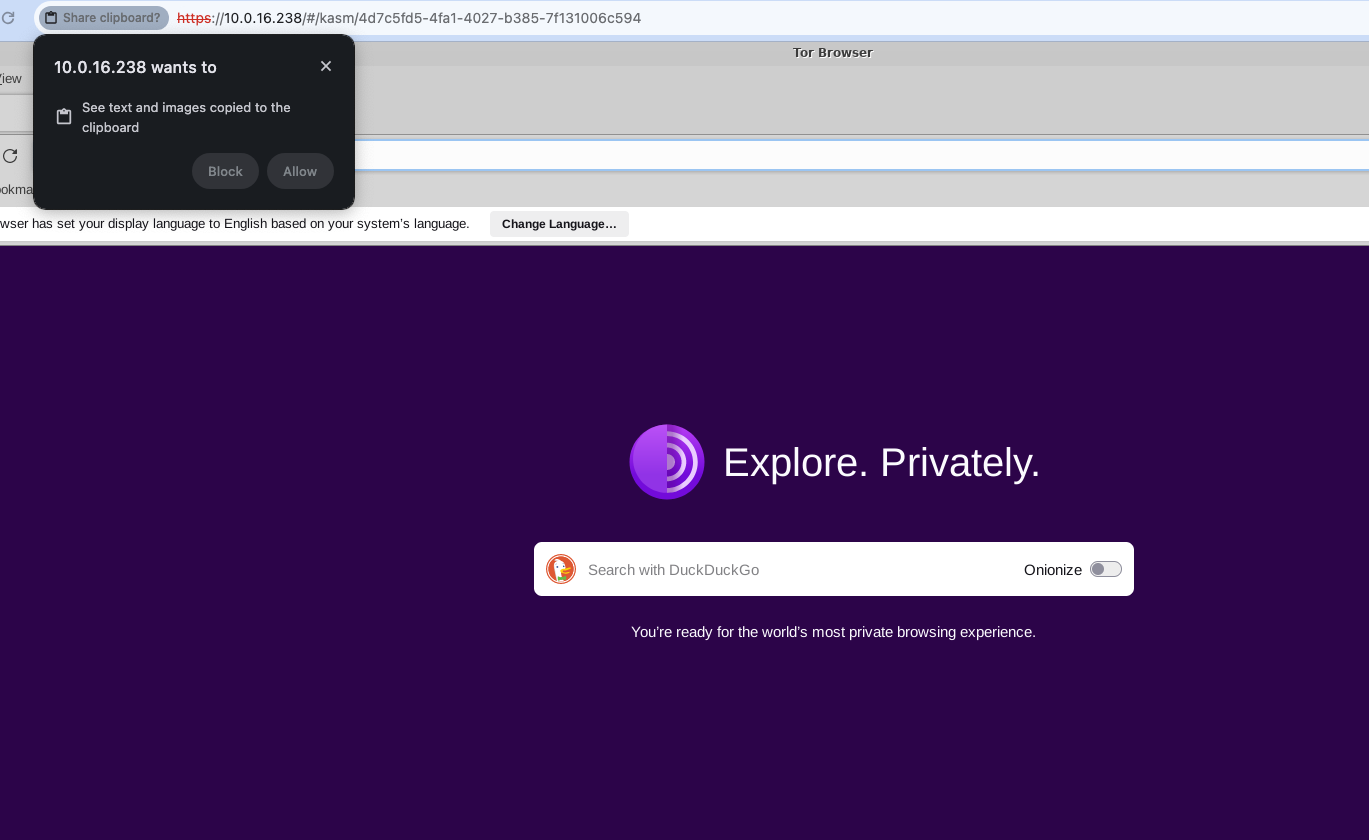
And we proceed to a web browser, I recommend using Google Chrome because it allows copying and pasting without modifying anything. We only allow access when prompted by the browser.
Now we will add applications
Steps
Login
Using the credentials from the CLI
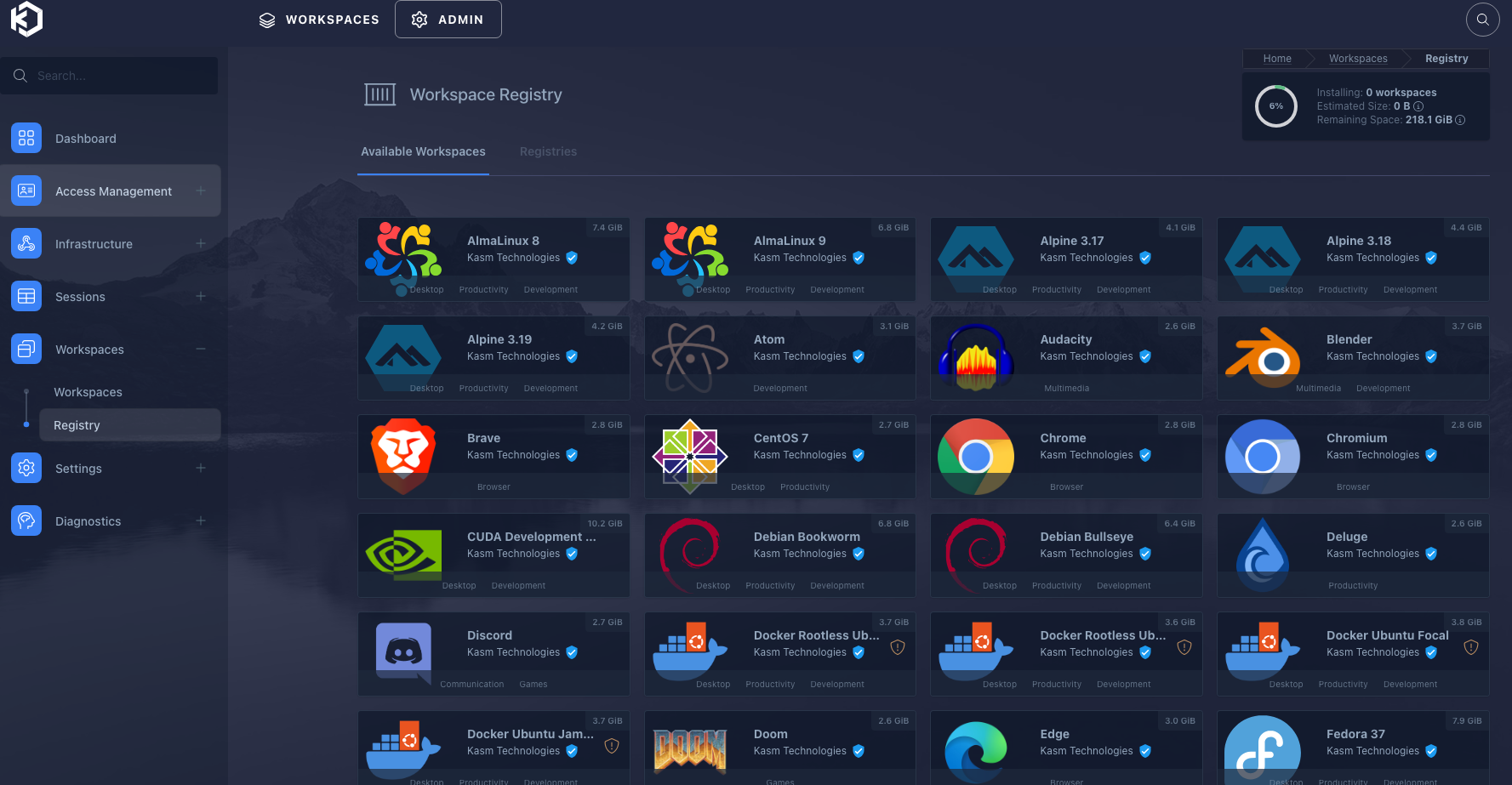
Registry
We need to update the registry simply by clicking on "Registry".
Install
Then we click on an app and the "install" button appears.
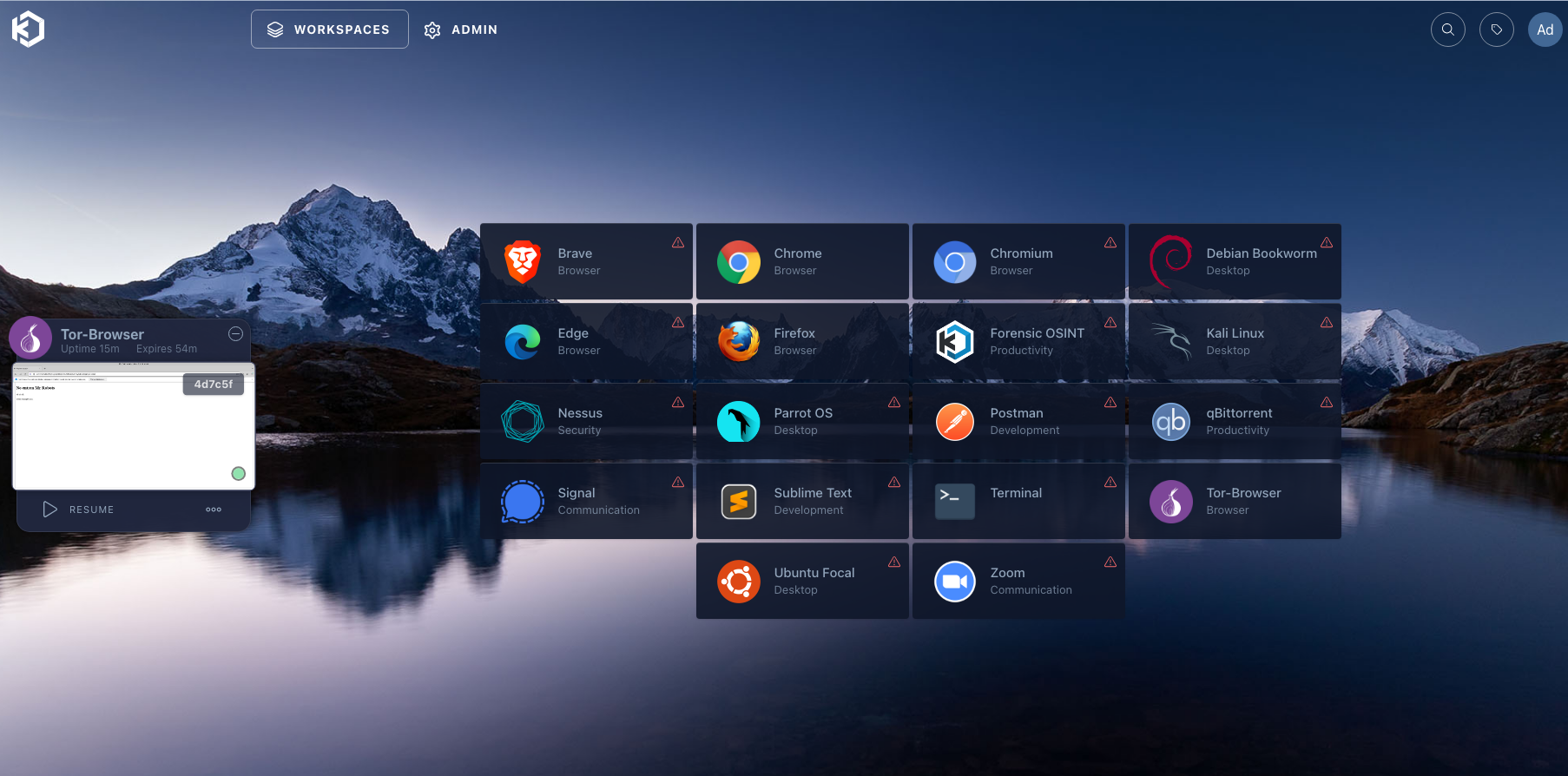
Workspace
We should wait for them to download, but if we click on the top where it says "Workspaces," we can access our applications.
Clipboard
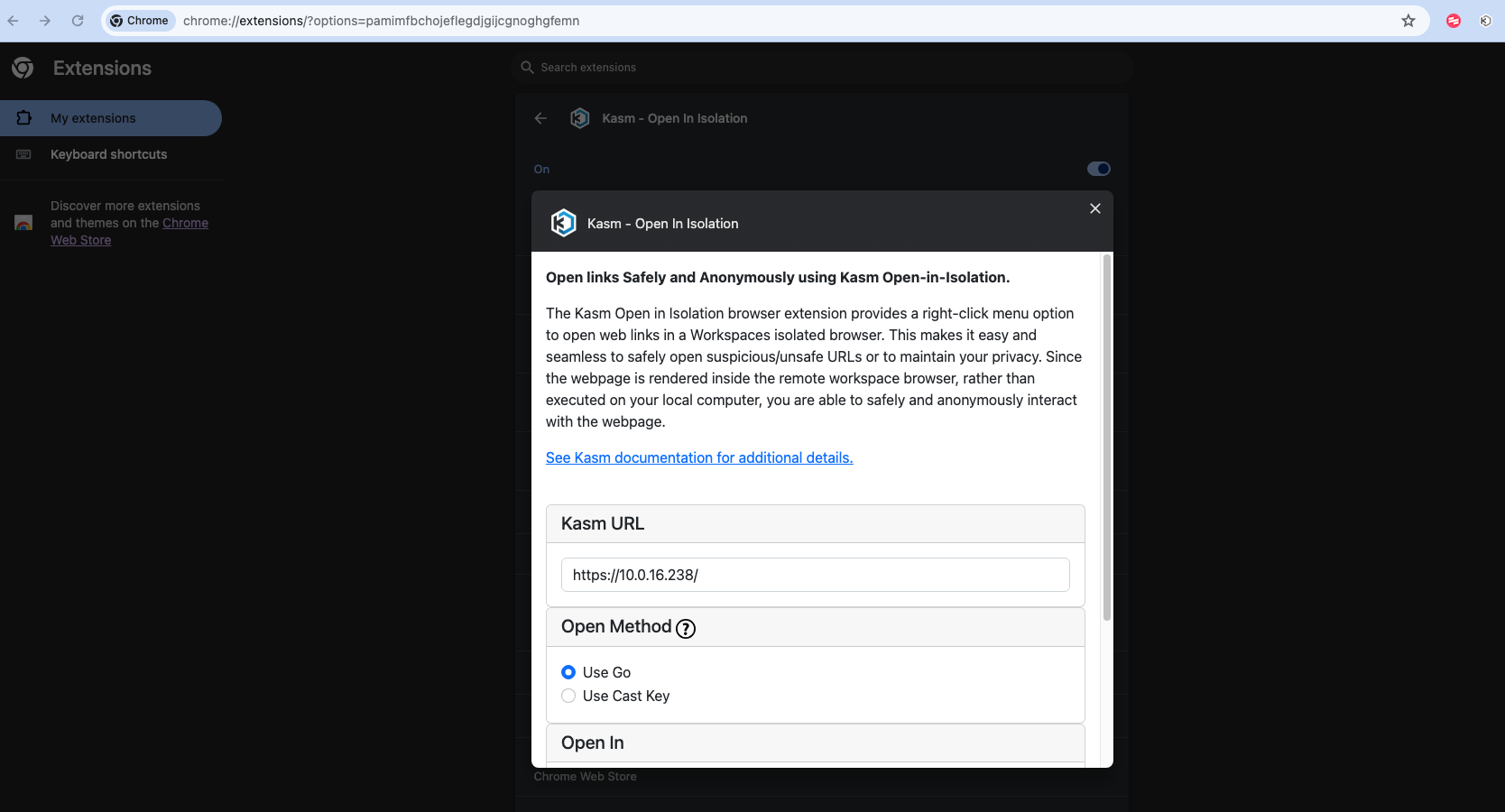
If we are using Google Chrome, we can easily copy links and also add the extension that allows us, with a simple right-click, to send a link to a browser within Kasm.
Extension
We can use the extension for easy access to links.
Terminals
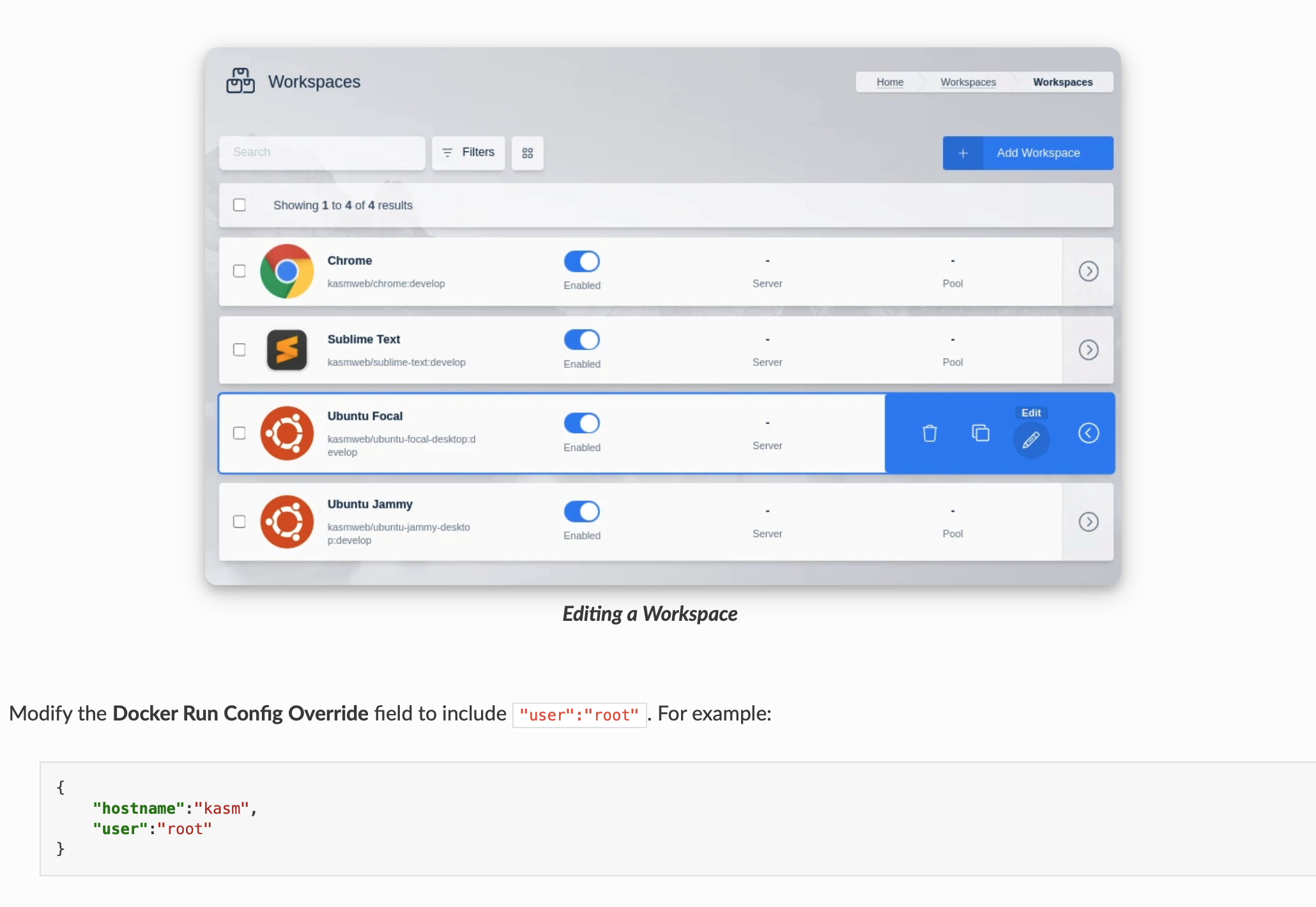
We need to modify the configuration file to have a personalized user and be able to install software or have root permissions.
Password
To reset the password in case it's lost, you need to log in again via the command line interface (CLI) and execute the following:
## reset password:
sudo docker exec -it kasm_db psql -U kasmapp -d kasm
update users set
pw_hash = 'fe519184b60a4ef9b93664a831502578499554338fd4500926996ca78fc7f522',
salt = '83d0947a-bf55-4bec-893b-63aed487a05e',
secret=NULL, set_two_factor=False, locked=False,
disabled=False, failed_pw_attempts = 0 where username ='admin@kasm.local';
DELETE FROM webauthn_credentials WHERE user_id IN ( SELECT user_id FROM users WHERE username = 'admin@kasm.local' );
\q
https://kasmweb.com/docs/latest/how_to/admin_account_recovery.html
Done, we're finished.
#!/bin/bash
# Lista de paquetes a instalar
paquetes=("docker.io" "docker-compose")
# Función para verificar si un paquete está instalado (Debian/Ubuntu/Kali)
paquete_instalado_apt() {
dpkg -l "$1" | grep -q '^ii'
}
# Función para verificar si un paquete está instalado (CentOS/RHEL)
paquete_instalado_yum() {
yum list installed "$1" &> /dev/null
}
# Función para verificar si un paquete está instalado (Fedora)
paquete_instalado_dnf() {
dnf list installed "$1" &> /dev/null
}
# Función para verificar si un paquete está instalado (Arch Linux)
paquete_instalado_pacman() {
pacman -Qi "$1" &> /dev/null
}
# Detectar el sistema operativo
if [ -f /etc/os-release ]; then
. /etc/os-release
OS=$ID
fi
# Instalar paquetes basados en el sistema operativo
for paquete in "${paquetes[@]}"; do
case $OS in
"debian"|"ubuntu"|"kali")
if ! paquete_instalado_apt "$paquete"; then
echo "Instalando el paquete $paquete..."
sudo apt-get install -y "$paquete"
fi
;;
"centos"|"rhel")
if ! paquete_instalado_yum "$paquete"; then
echo "Instalando el paquete $paquete..."
sudo yum install -y "$paquete"
fi
;;
"fedora")
if ! paquete_instalado_dnf "$paquete"; then
echo "Instalando el paquete $paquete..."
sudo dnf install -y "$paquete"
fi
;;
"arch")
if ! paquete_instalado_pacman "$paquete"; then
echo "Instalando el paquete $paquete..."
sudo pacman -S --noconfirm "$paquete"
fi
;;
*)
;;
esac
done
# Pedir al usuario cuántos GB de RAM desea
read -p "Cuanto de GB de RAM desea ( 4, 6, 8...) : " ram_gb
# Calcular el tamaño del archivo de swap en MB
swap_size_mb=$((ram_gb * 1024))
# Crear un archivo de swap del tamaño calculado
sudo dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count="$swap_size_mb" of=/mnt/"$ram_gb"GiB.swap
sudo chmod 600 /mnt/"$ram_gb"GiB.swap
sudo mkswap /mnt/"$ram_gb"GiB.swap
sudo swapon /mnt/"$ram_gb"GiB.swap
# Hacer que el archivo de swap esté disponible en el arranque
echo "/mnt/$ram_gb GiB.swap swap swap defaults 0 0" | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
# Descargar e instalar Kasm
cd /tmp
curl -O https://kasm-static-content.s3.amazonaws.com/kasm_release_1.15.0.06fdc8.tar.gz
tar -xf kasm_release_1.15.0.06fdc8.tar.gz
sudo bash kasm_release/install.sh