Creating an Ephemeral Firefox Browser with Docker
In this guide, we'll create a disposable Firefox browser using Docker that automatically destroys its session after use. This is perfect for opening potentially risky links without leaving traces on your system.
Note: It is very useful because it allows changing the Firefox language, which helps avoid browser detection.
Step 1: Create the Dockerfile
First, let's create a Dockerfile that will set up our ephemeral Firefox environment:
root@kali:~/firefox-ephemeral# cat Dockerfile FROM debian:bookworm ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive RUN apt-get update && \ apt-get install -y \ firefox-esr \ libgtk-3-0 \ libdbus-glib-1-2 \ libx11-xcb1 \ libasound2 \ x11-utils && \ apt-get clean && \ rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* ENTRYPOINT ["firefox-esr"]
Step 2: Build the Docker Image
Build the Docker image with the following command:
root@kali:~/firefox-ephemeral# docker build -t firefox-ephemeral . Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.048kB Step 1/3 : FROM debian:bookworm ---> 1234567890ab Step 2/3 : ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive ---> Running in abcdef123456 Step 3/3 : RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y firefox-esr libgtk-3-0 libdbus-glib-1-2 libx11-xcb1 libasound2 x11-utils && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* ---> Running in 7890abcdef12 Successfully built 1234567890ab Successfully tagged firefox-ephemeral:latest
Step 3: Install XQuartz
Install XQuartz using Homebrew:
user@mac:~# brew install --cask xquartz ==> Downloading https://dl.bintray.com/xquartz/downloads/XQuartz-2.8.1.dmg ######################################################################## 100.0% ==> Installing Cask xquartz ==> Moving App 'XQuartz.app' to '/Applications/XQuartz.app' ==> Linking Binary 'xauth' to '/usr/local/bin/xauth' ==> Linking Binary 'xhost' to '/usr/local/bin/xhost' ==> Linking Binary 'xmodmap' to '/usr/local/bin/xmodmap' ==> Linking Binary 'xrdb' to '/usr/local/bin/xrdb' ==> Linking Binary 'xset' to '/usr/local/bin/xset' ==> Linking Binary 'xsetroot' to '/usr/local/bin/xsetroot' ==> Linking Binary 'xterm' to '/usr/local/bin/xterm'
Step 4: Configure X11
Run these commands in your terminal:
user@mac:~# export DISPLAY=:0 user@mac:~# /opt/X11/bin/xhost + 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 being added to access control list
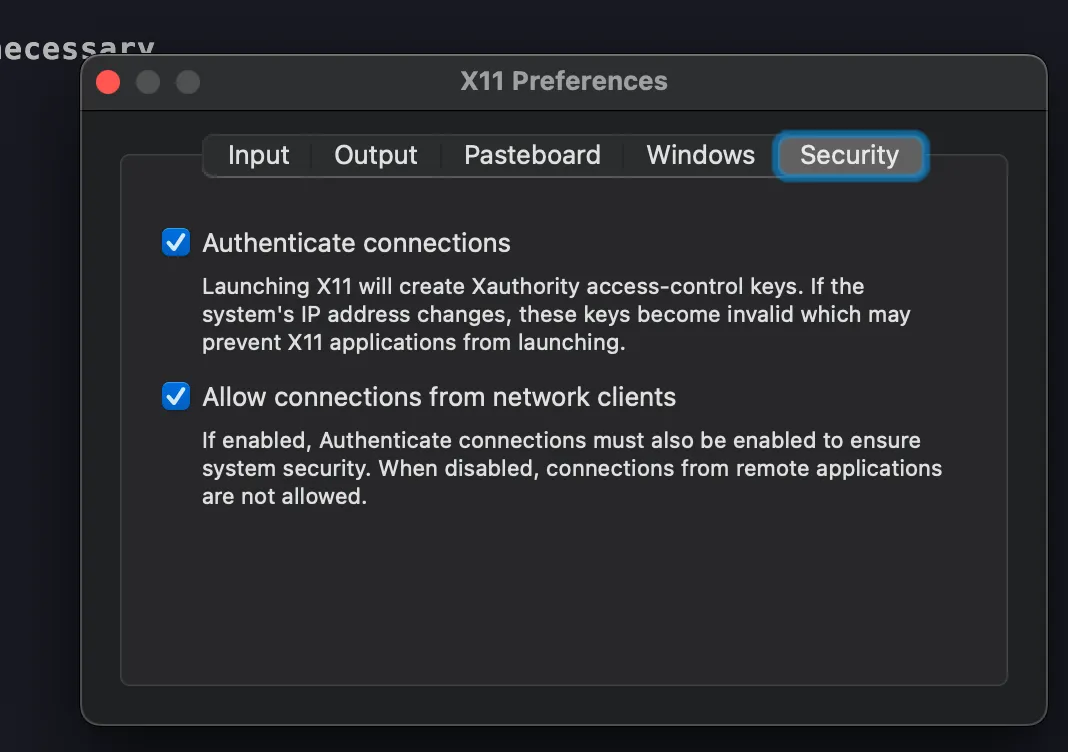
Open X11 preferences and enable "Allow connections from network clients". IMPORTANT: After enabling network clients in X11, you must restart your machine for the changes to take effect.
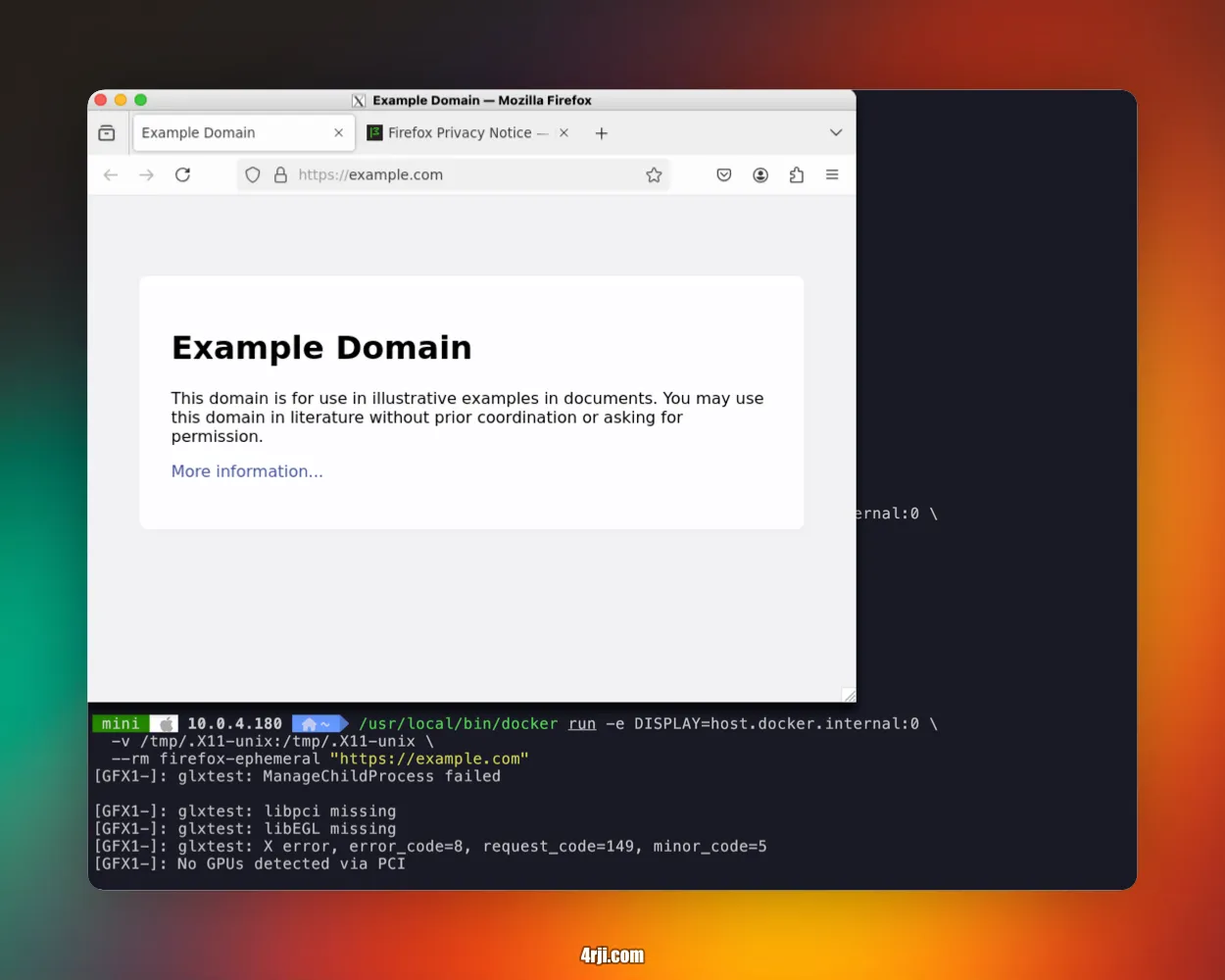
Step 5: Test the Setup
Test if everything works by running:
/usr/local/bin/docker run -e DISPLAY=host.docker.internal:0 \ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \ --rm firefox-ephemeral "https://4rji.com"
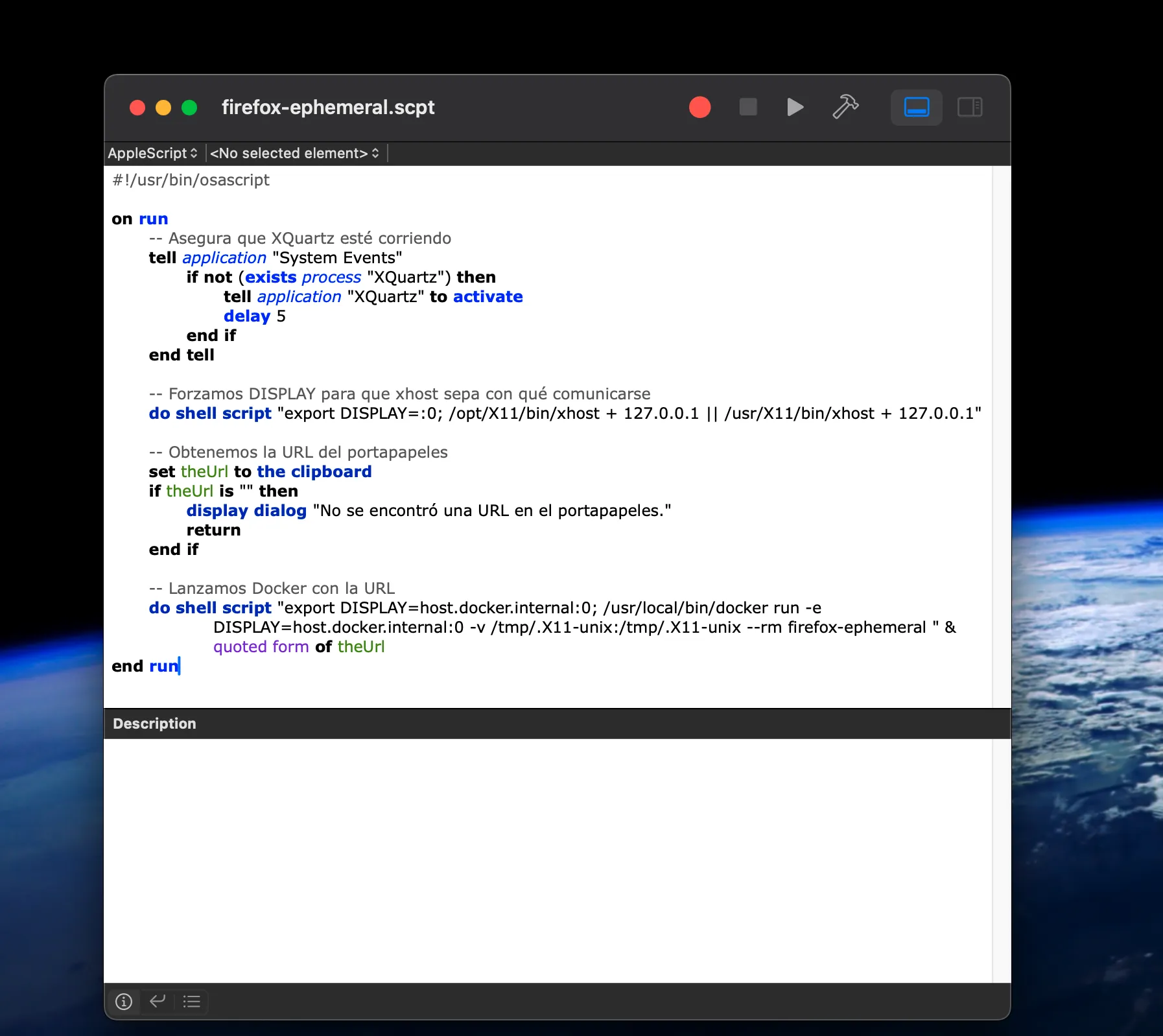
Step 6: Create an Automation Script